EMG (electromyography) is a technique used to measure electrical signals (action potentials) in muscle fibres. The signals are the result of electrical excitation of the muscle by the motor control systems of the nervous system transmitted to muscles by motor nerves. Motor action potentials trigger muscle contraction by a process known as excitation-contraction coupling.
The EMG signal is a direct measure of the neural drive to the muscle and an indirect estimate of the contraction force generated by the neural drive.
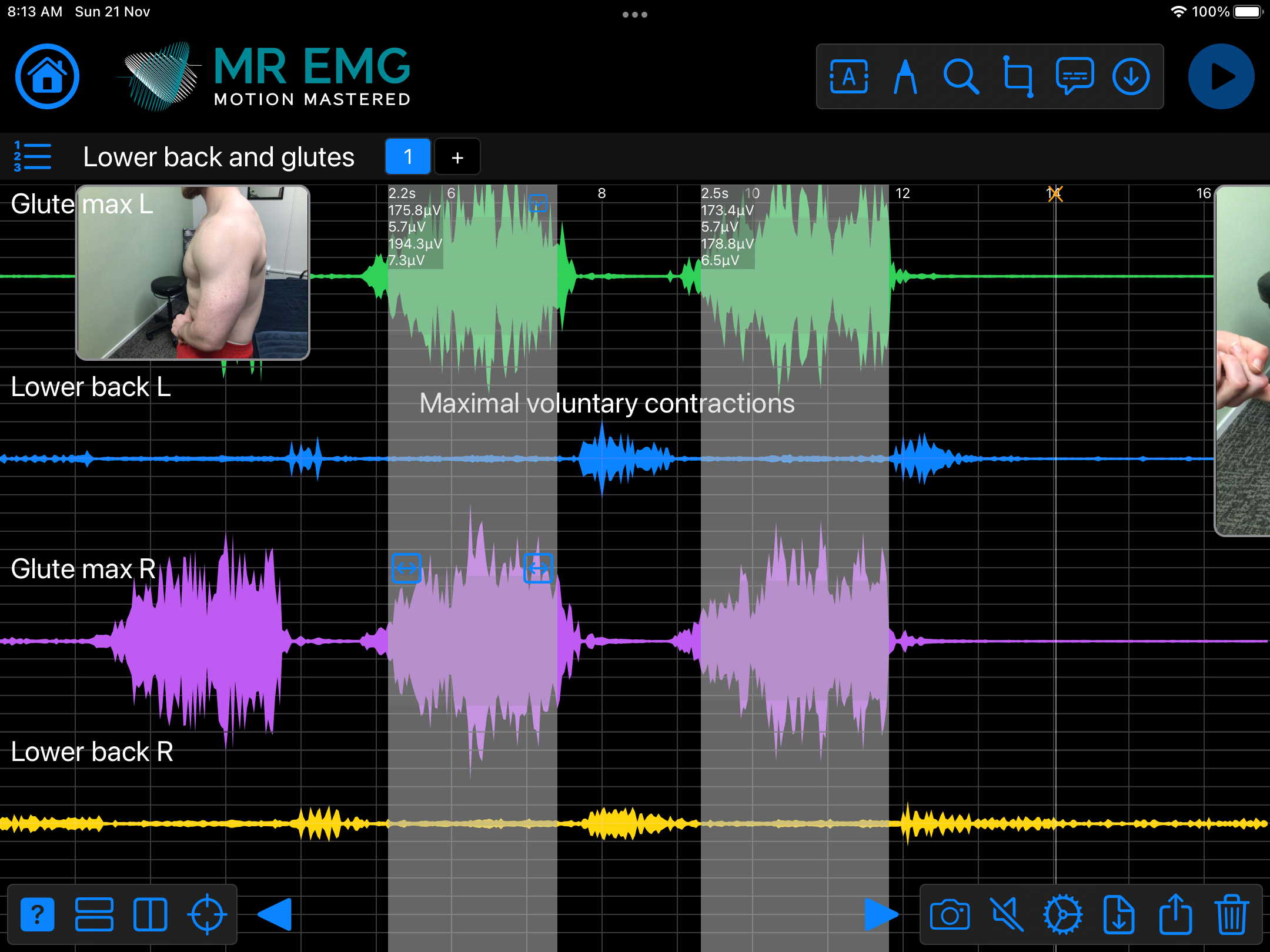
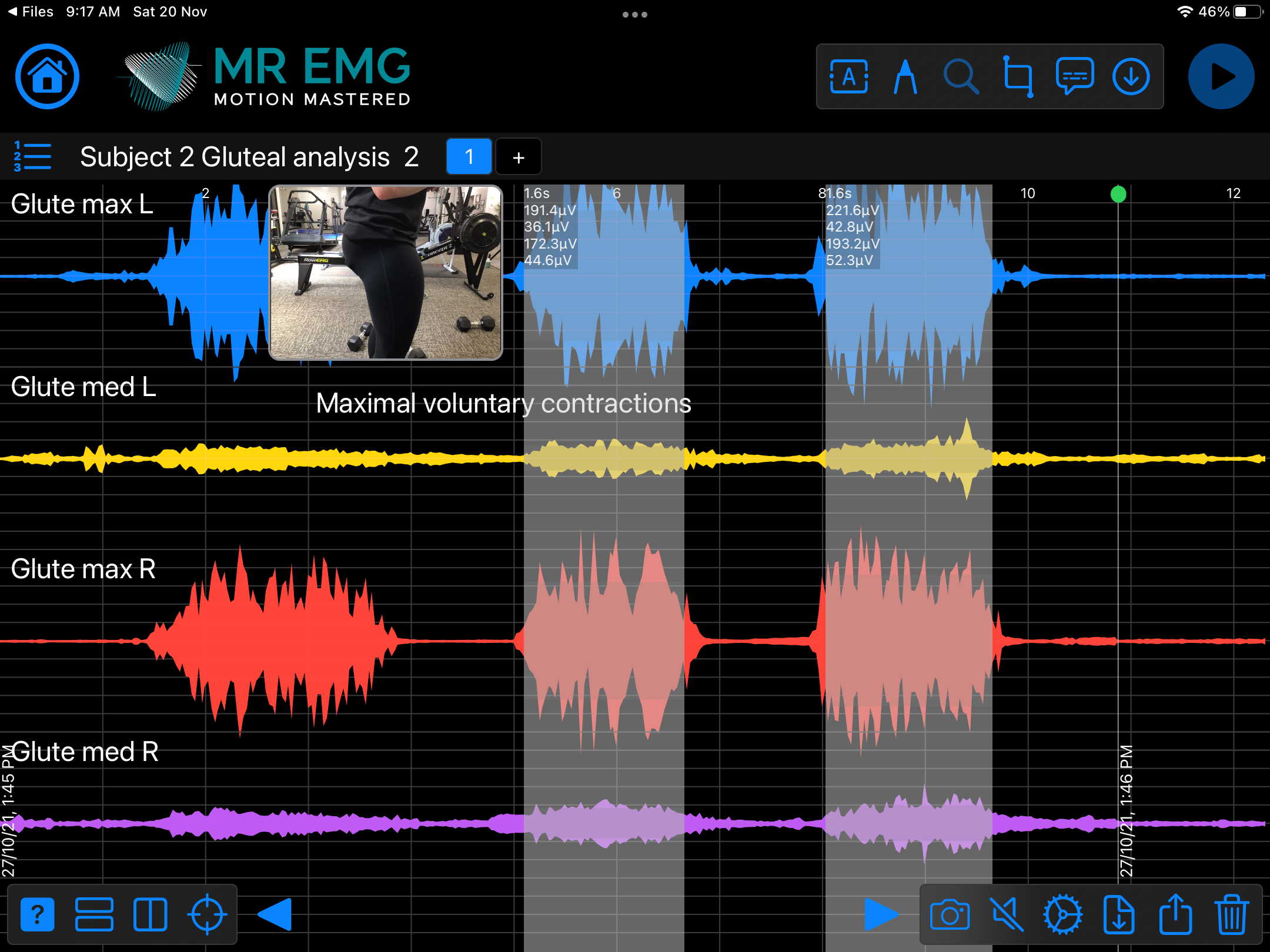
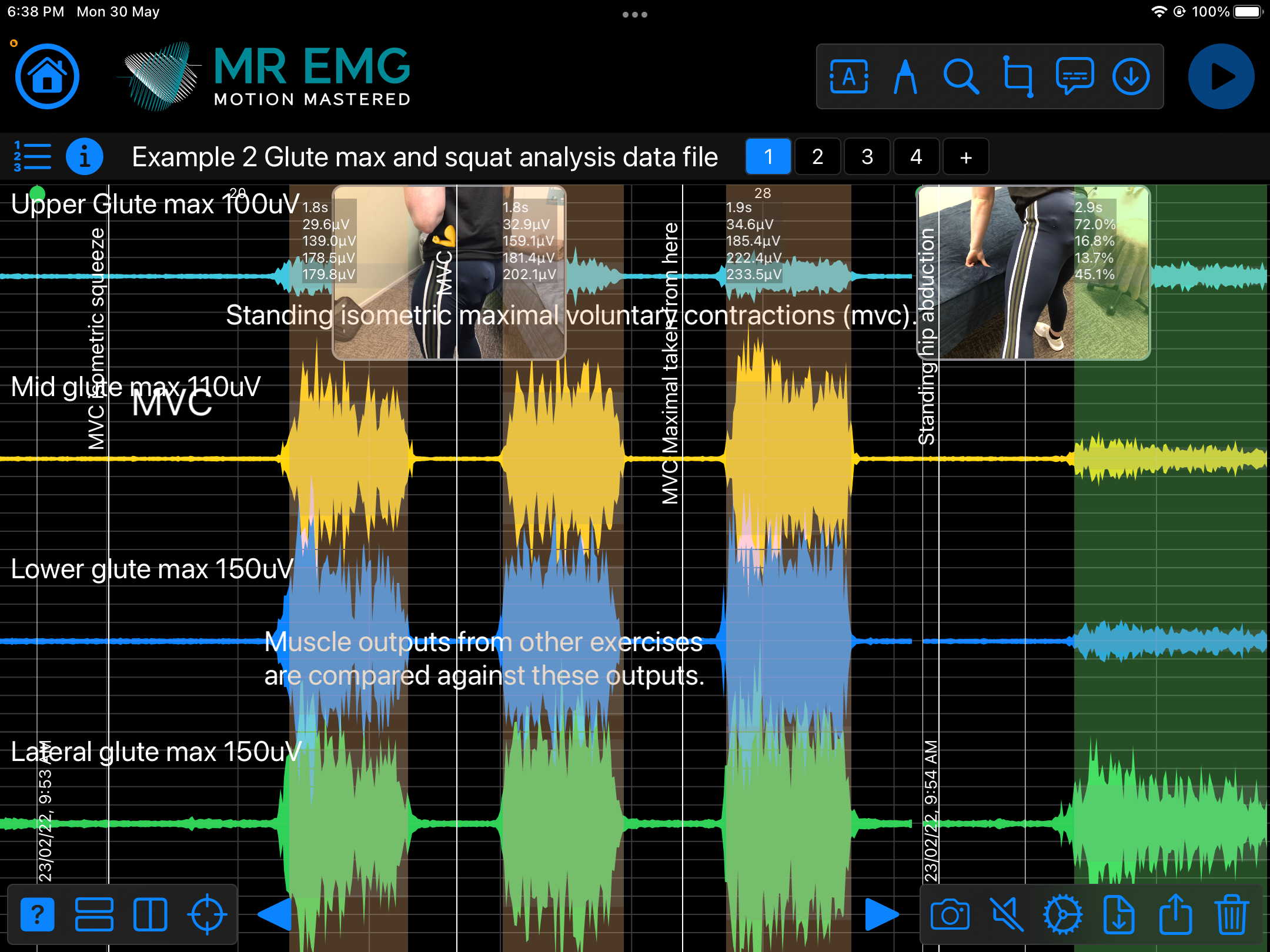
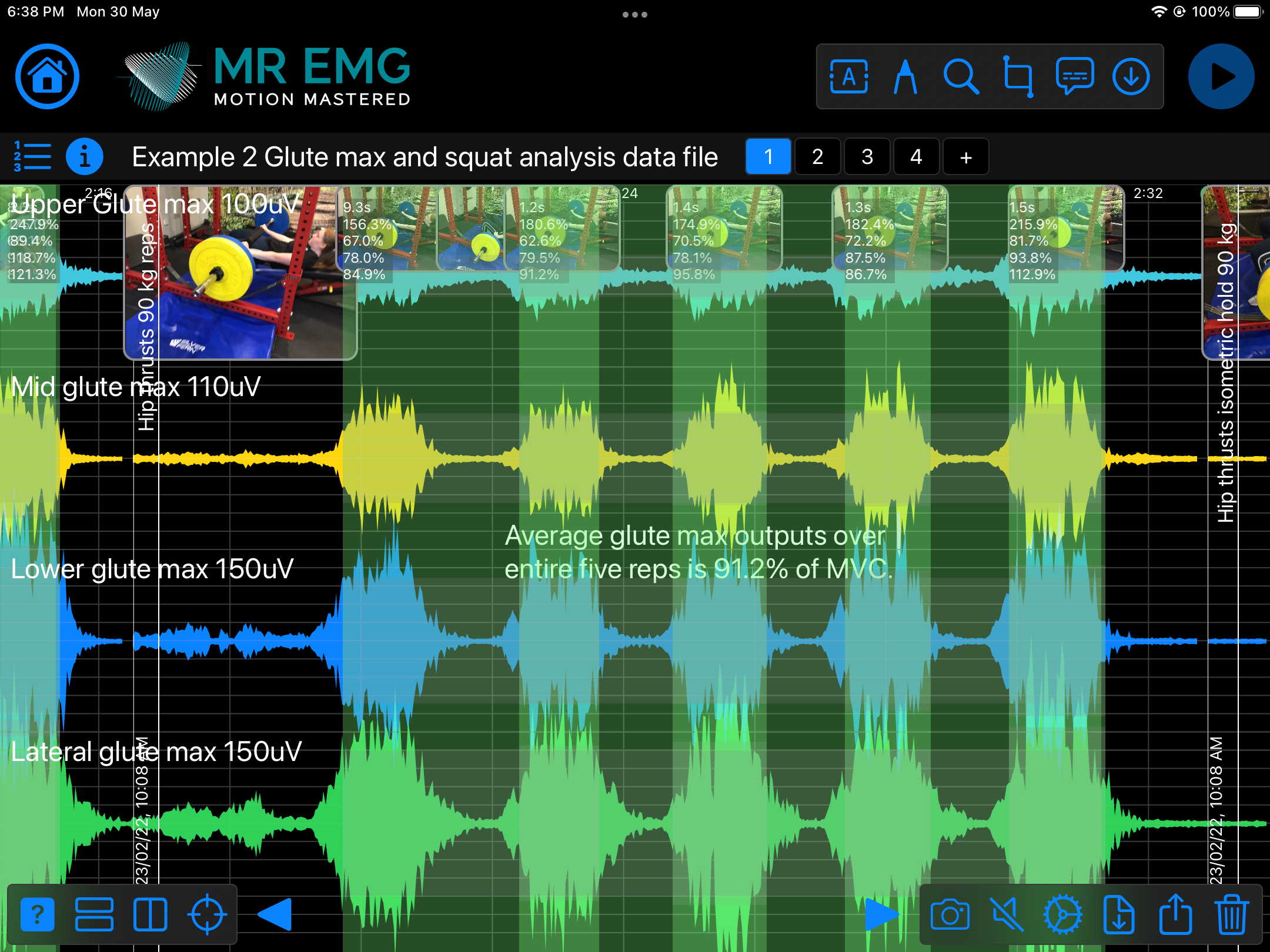
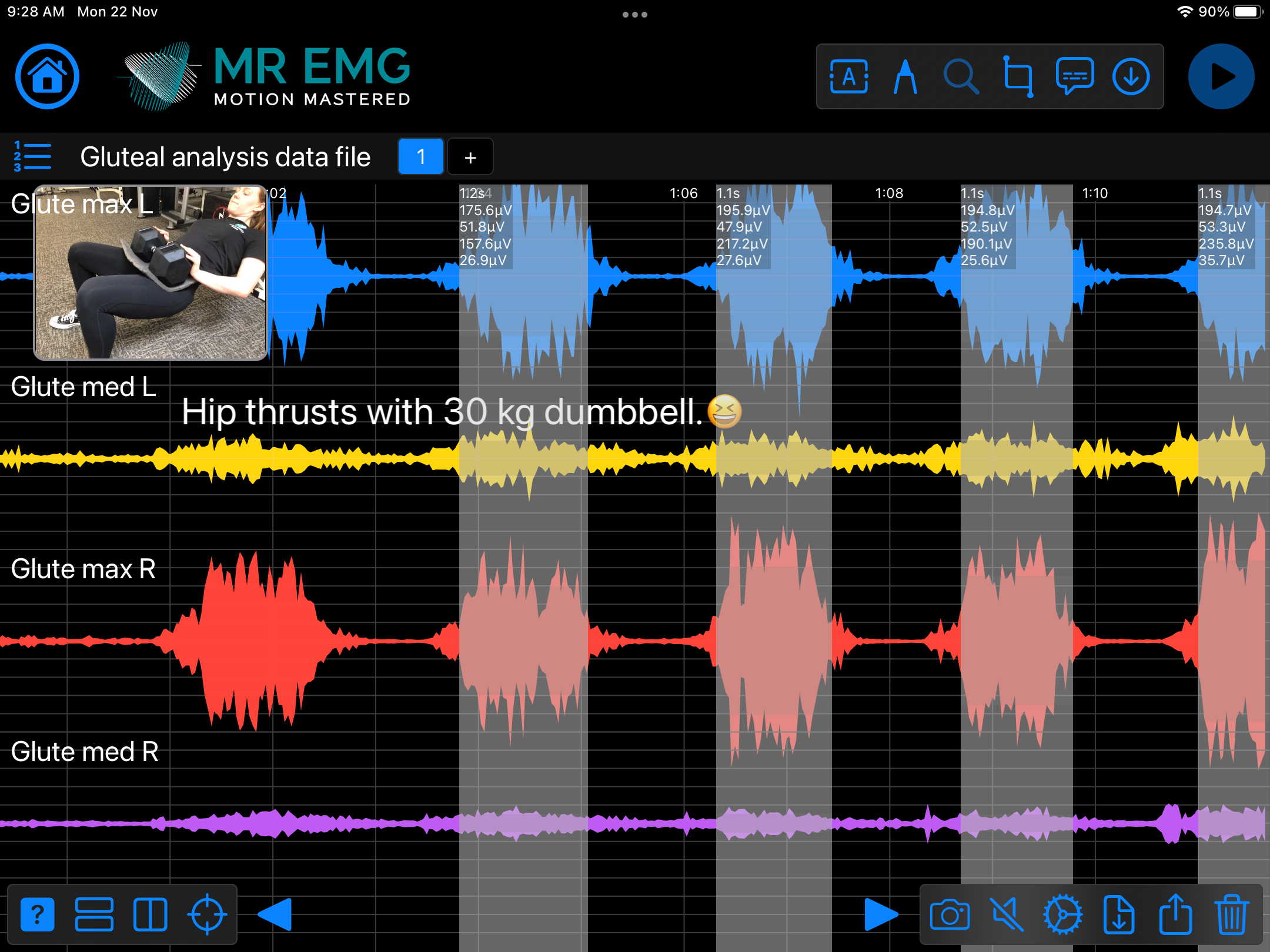
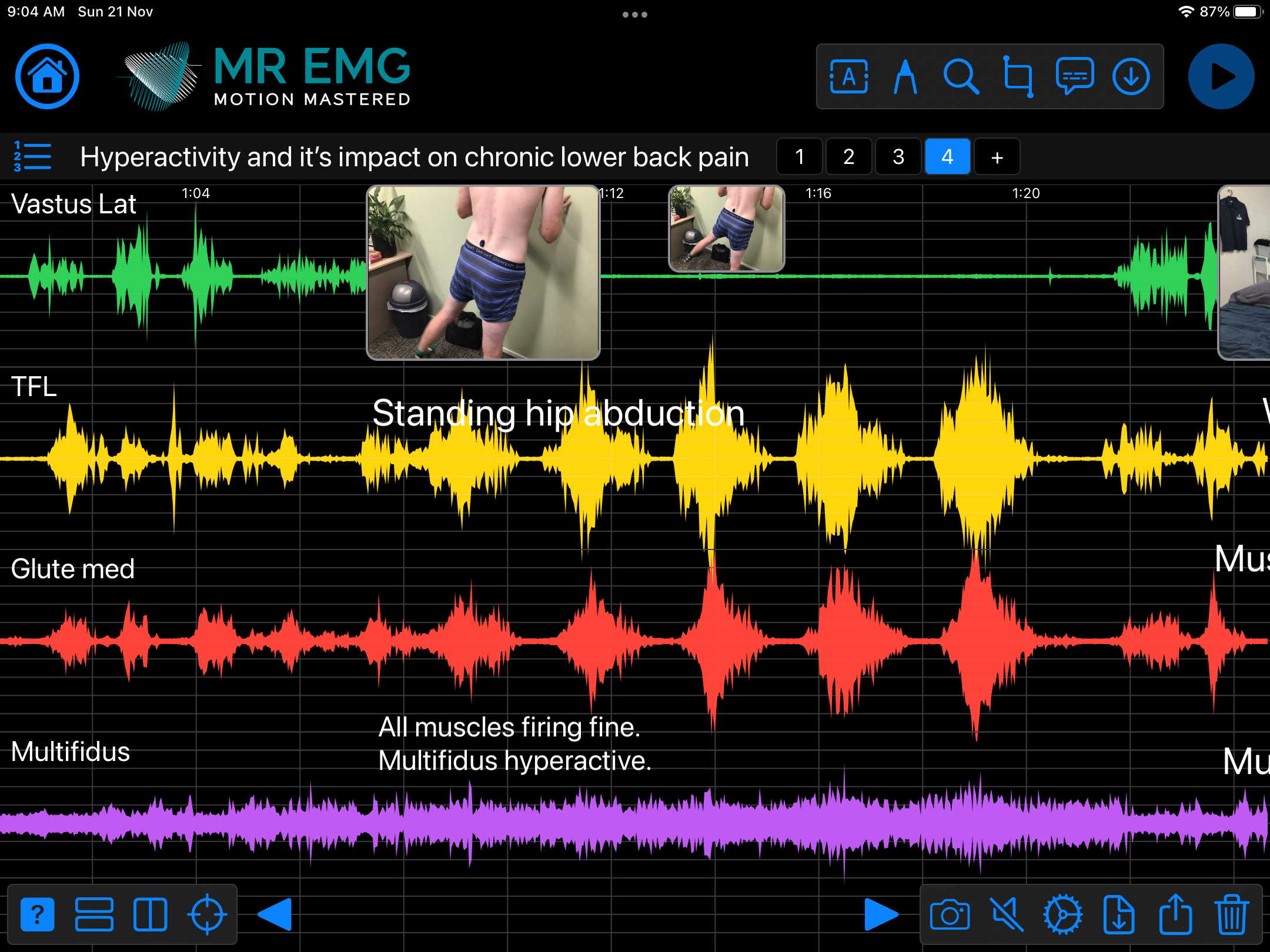
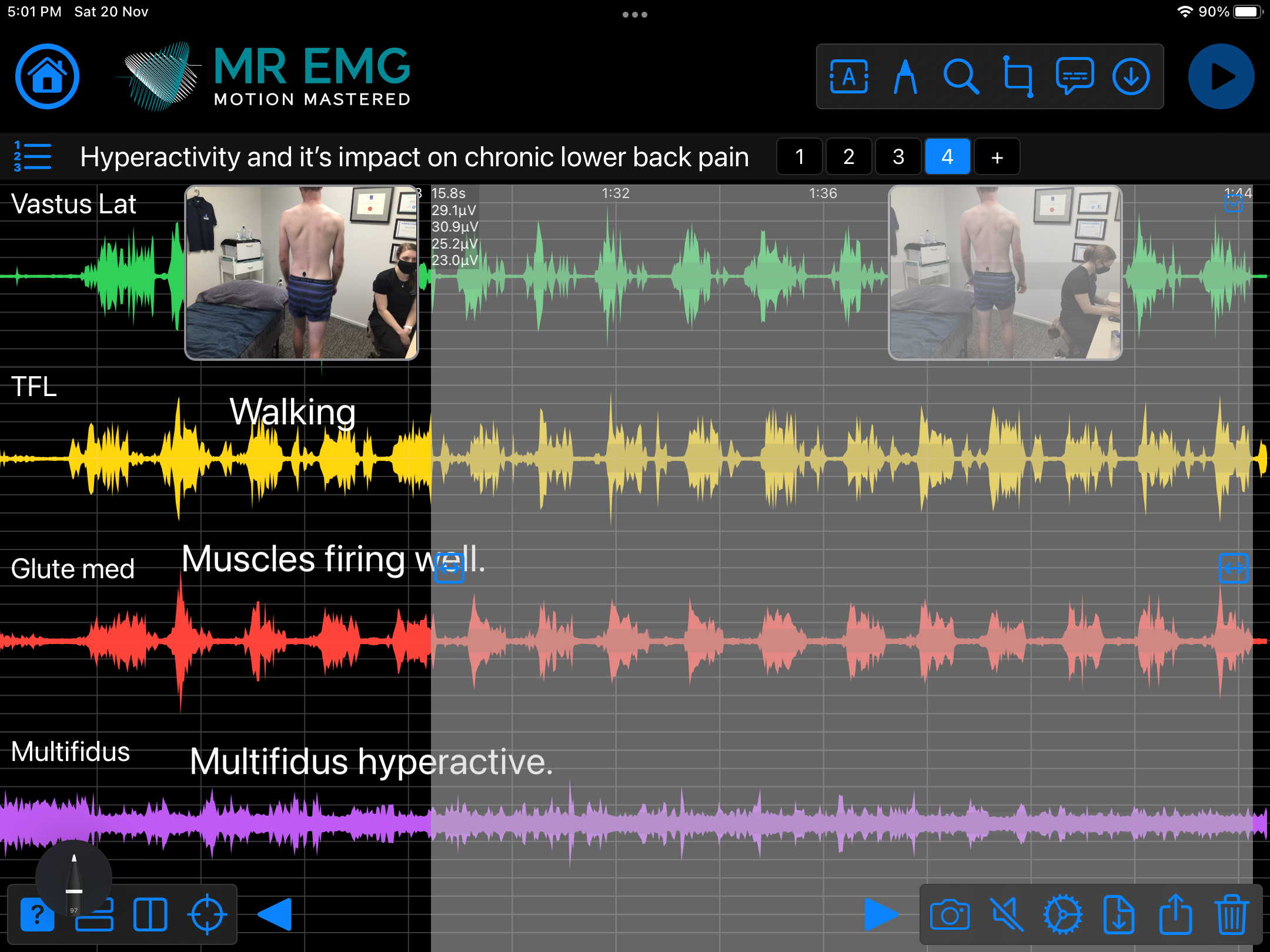
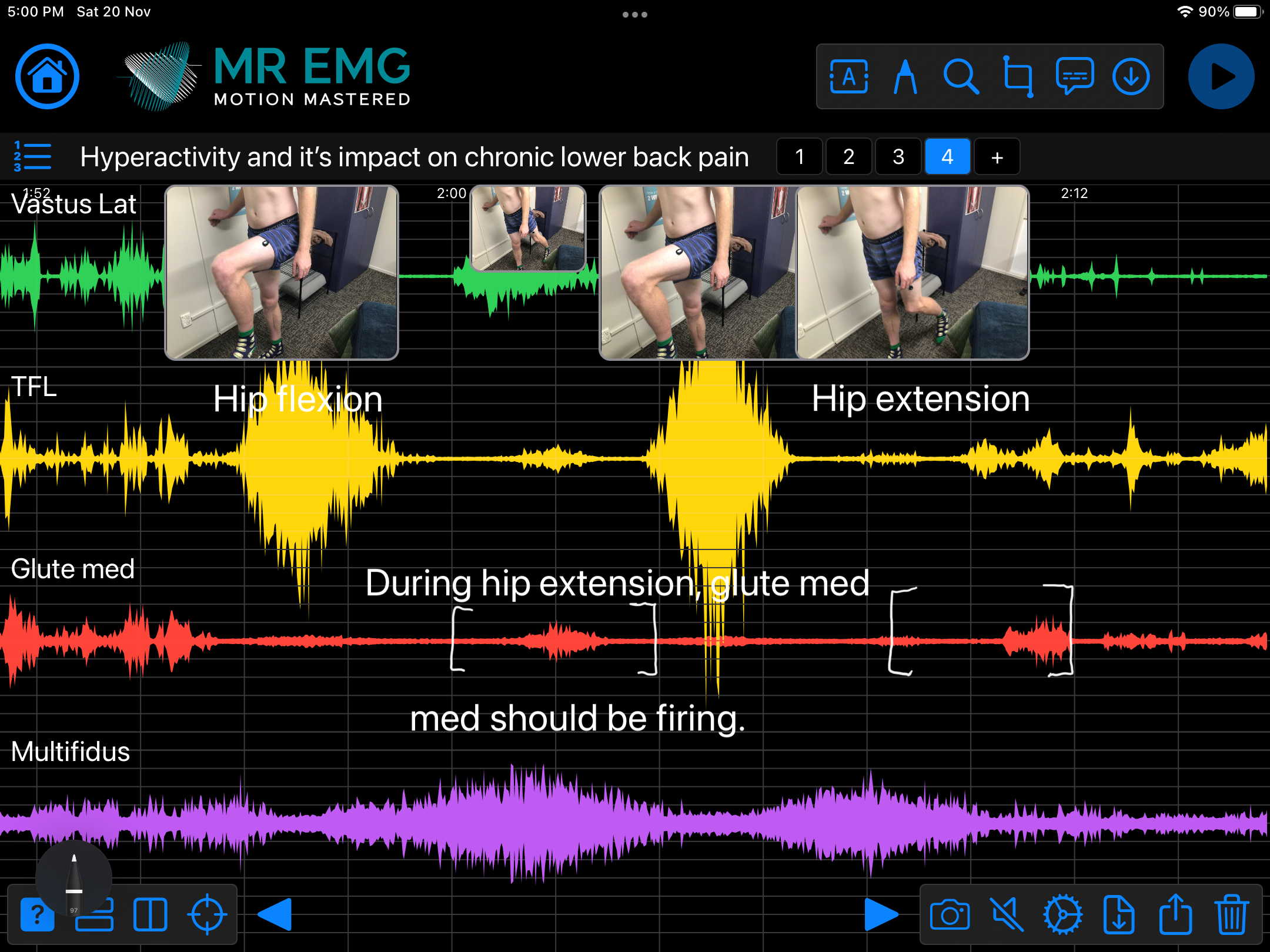
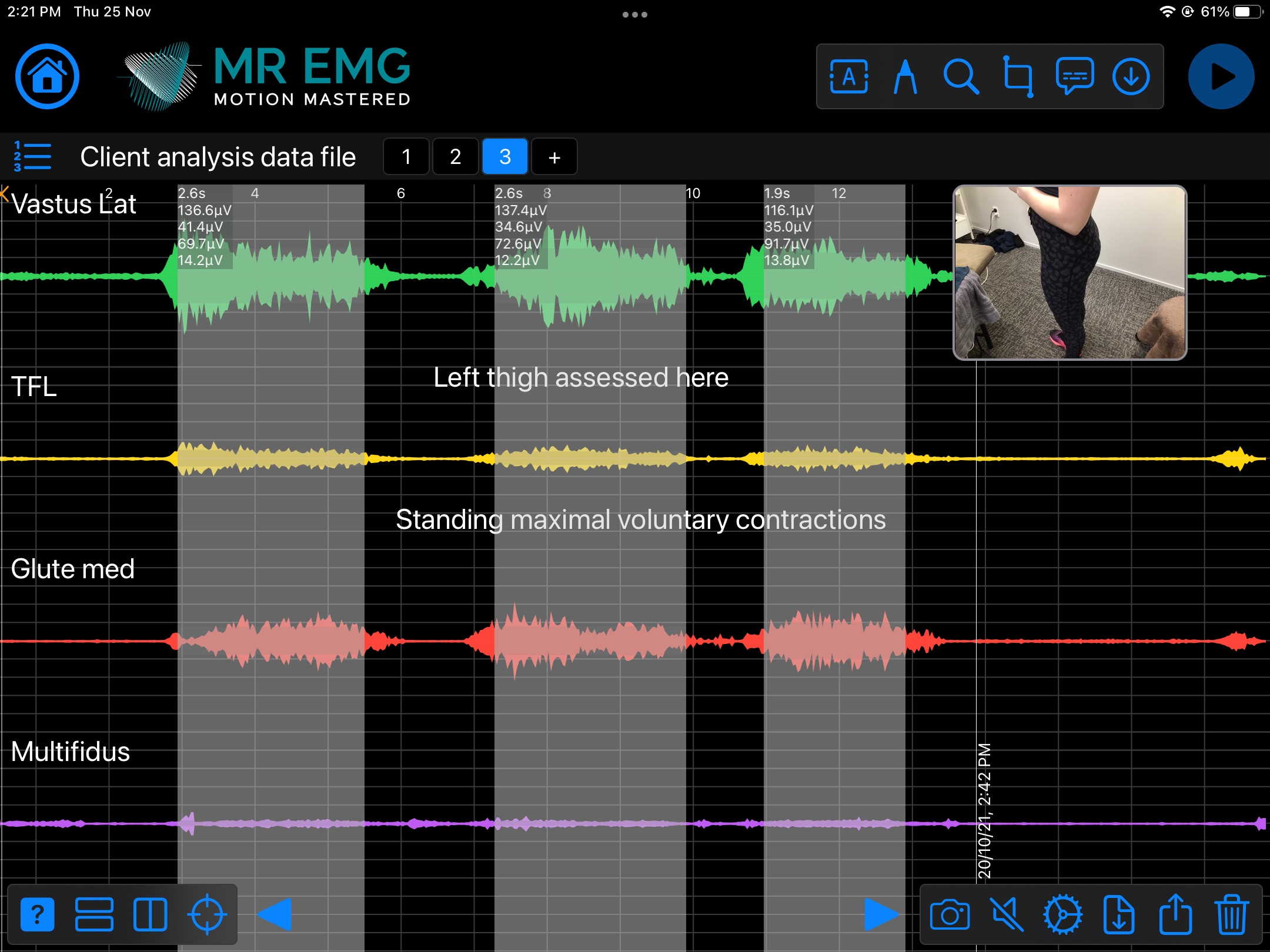
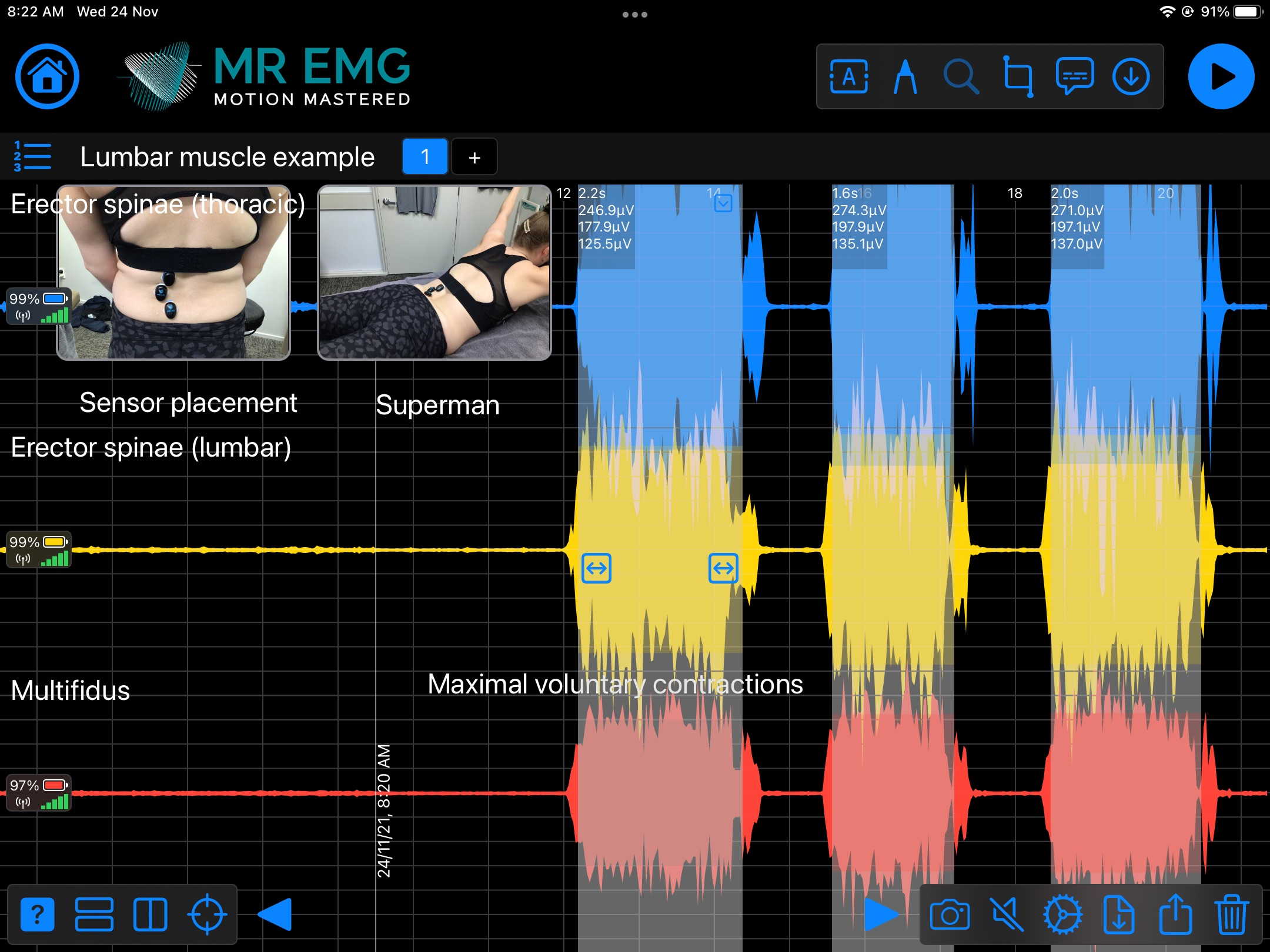
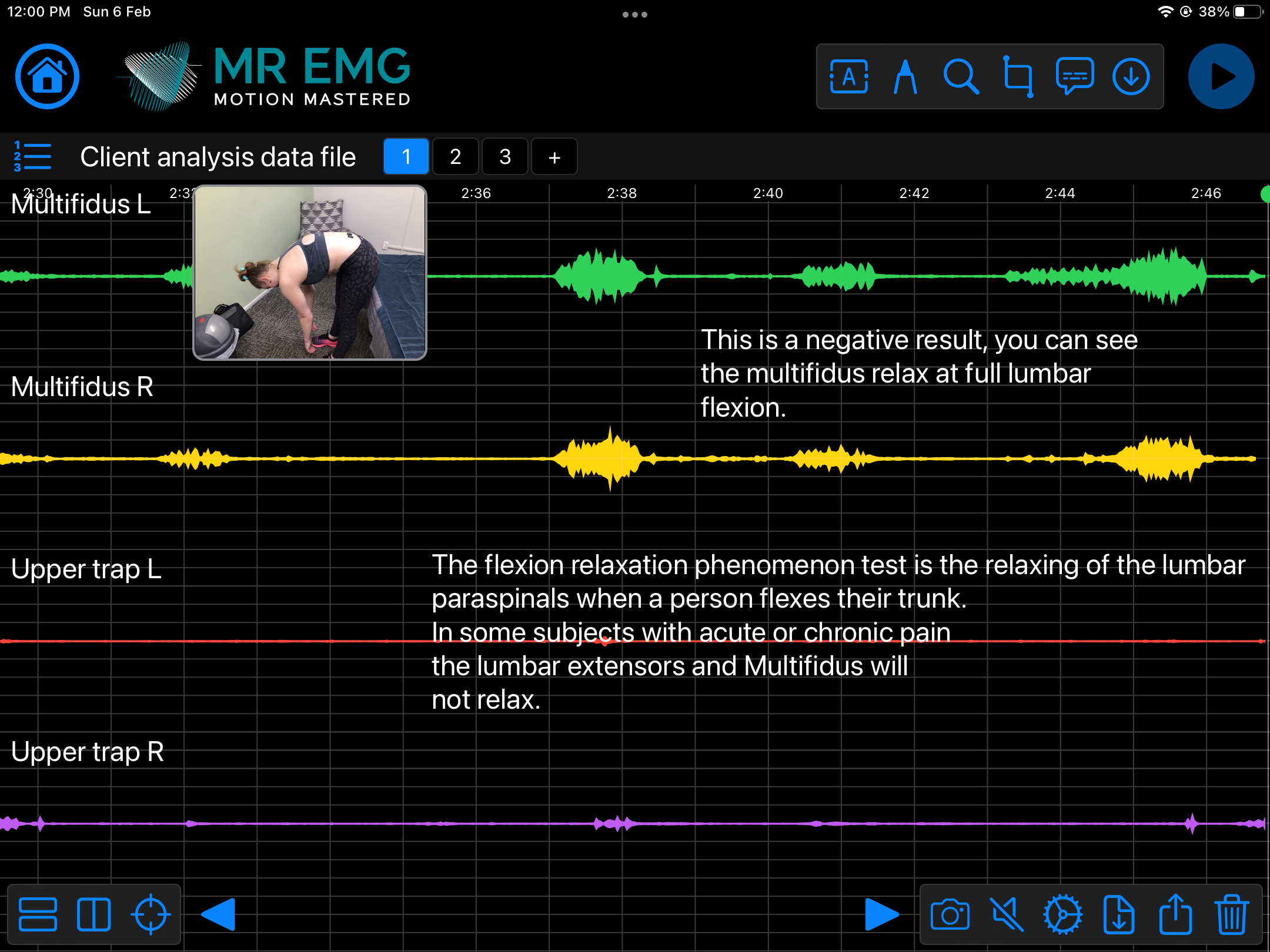
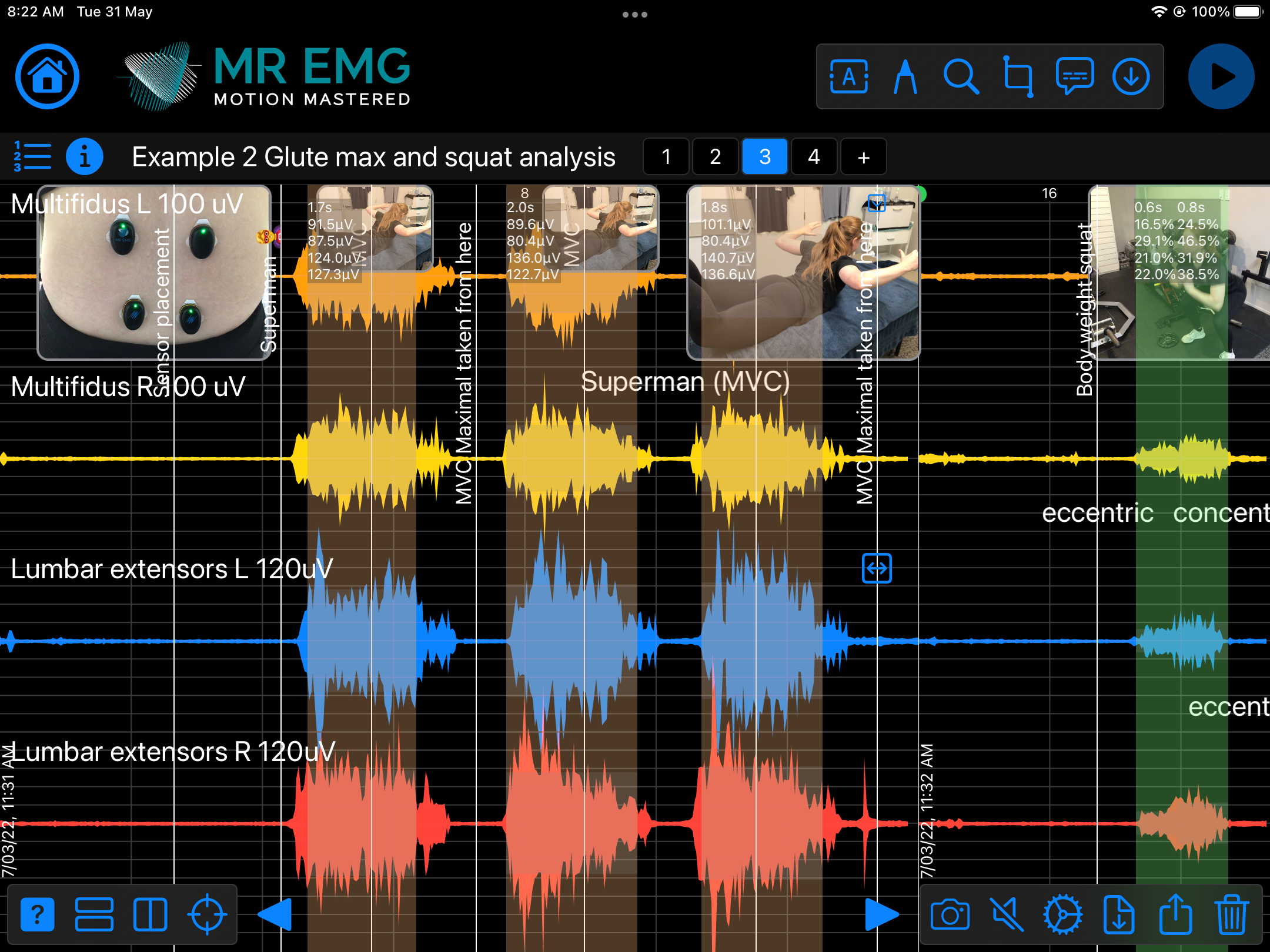
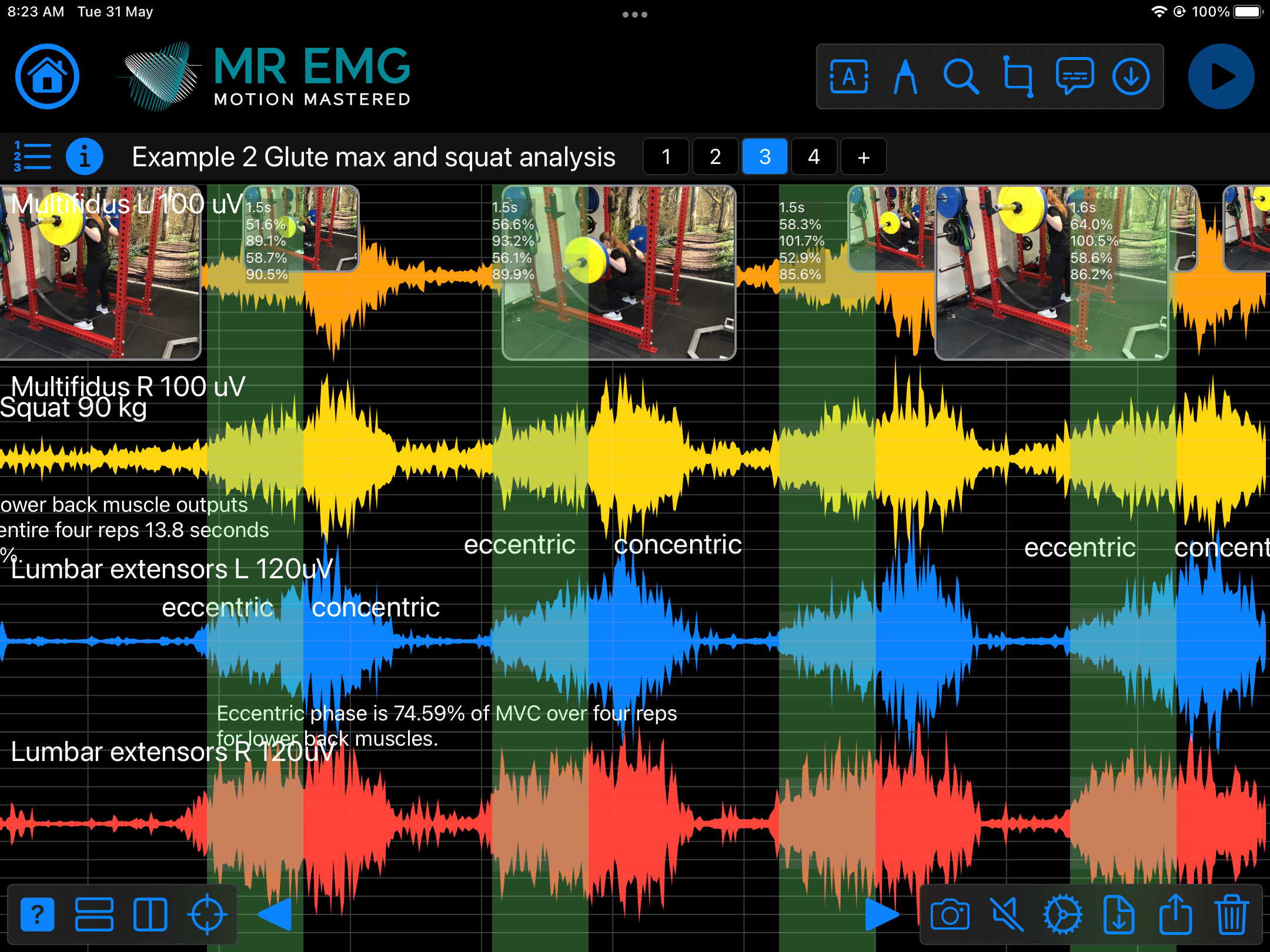
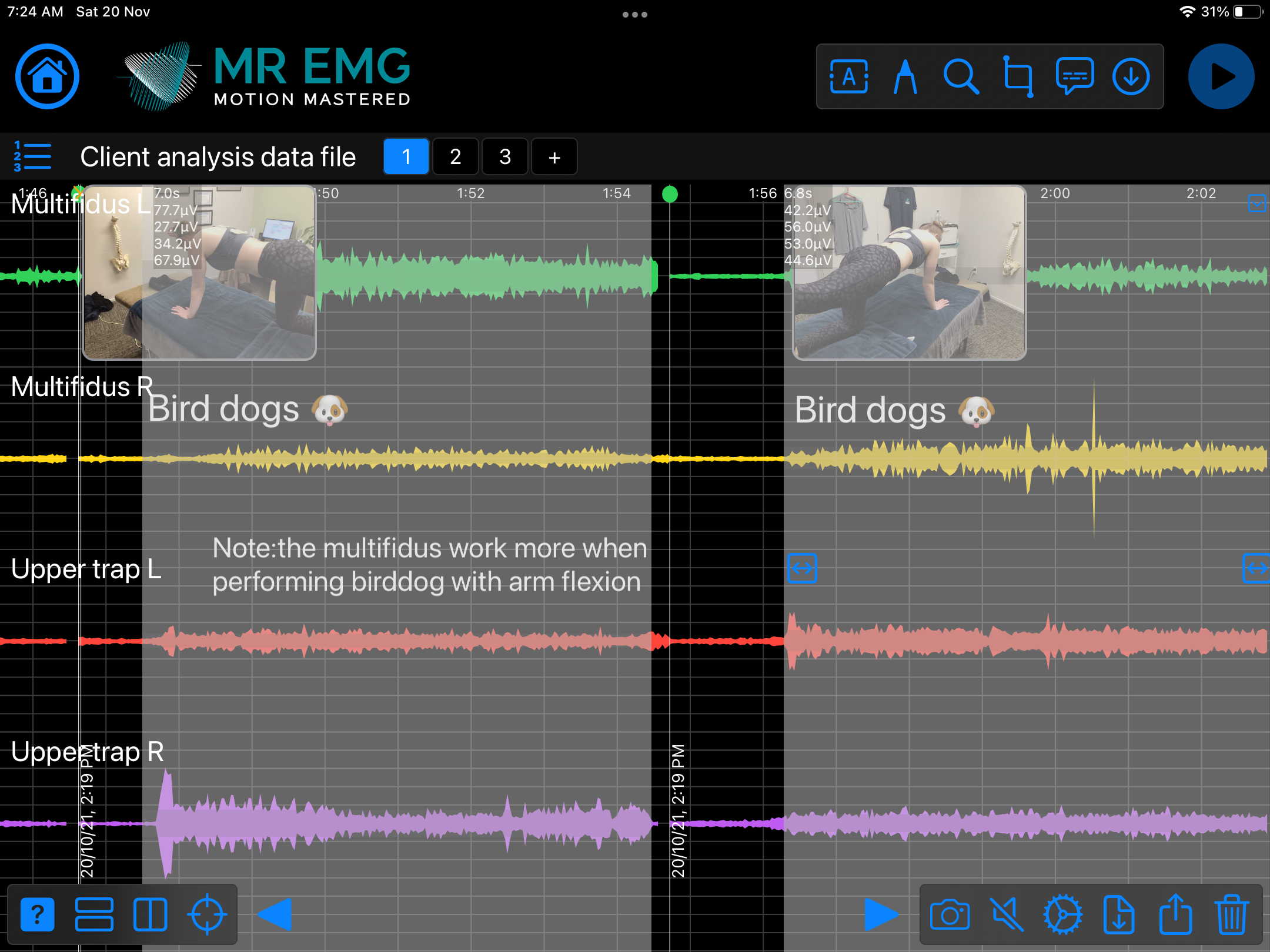
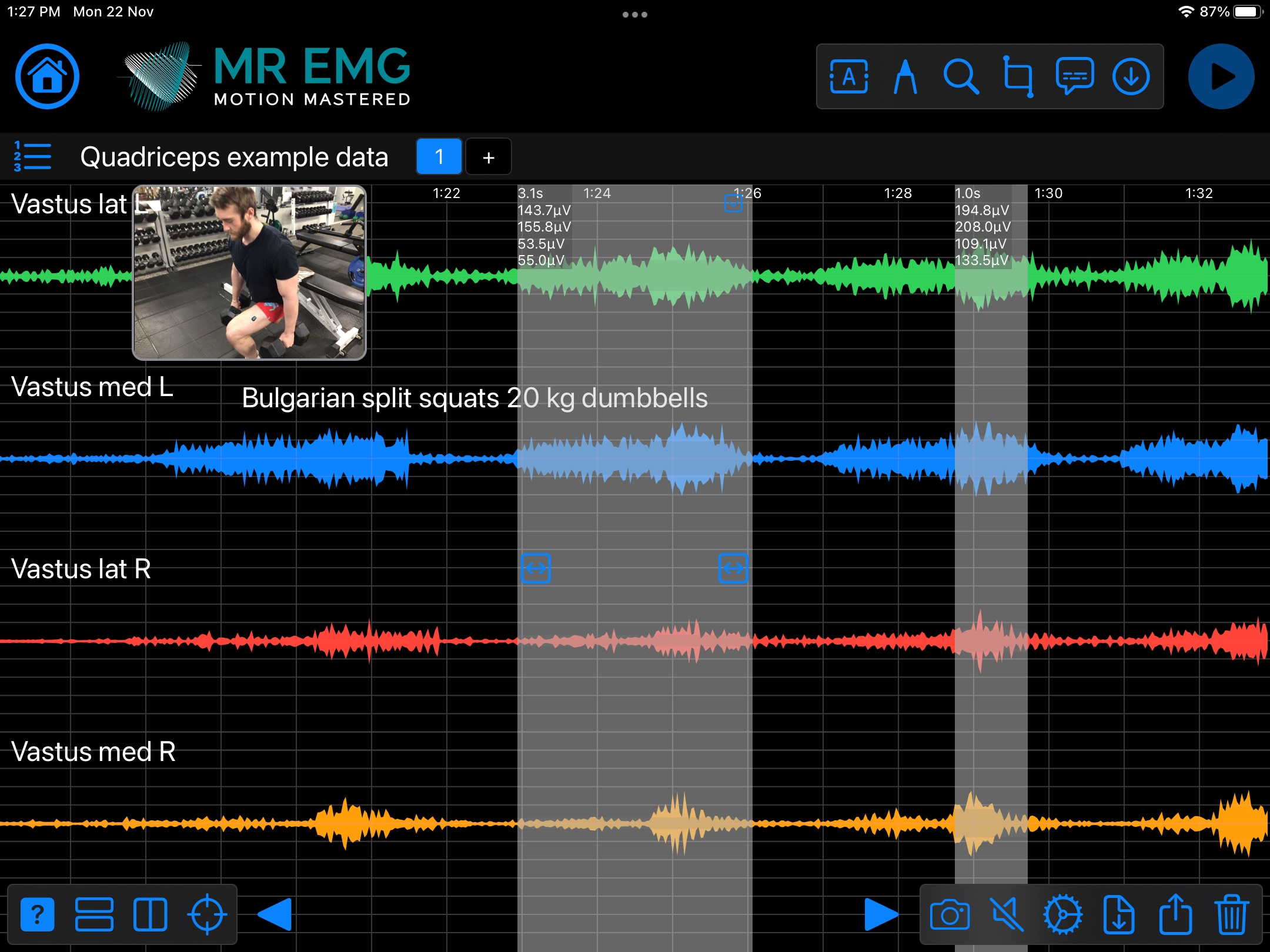
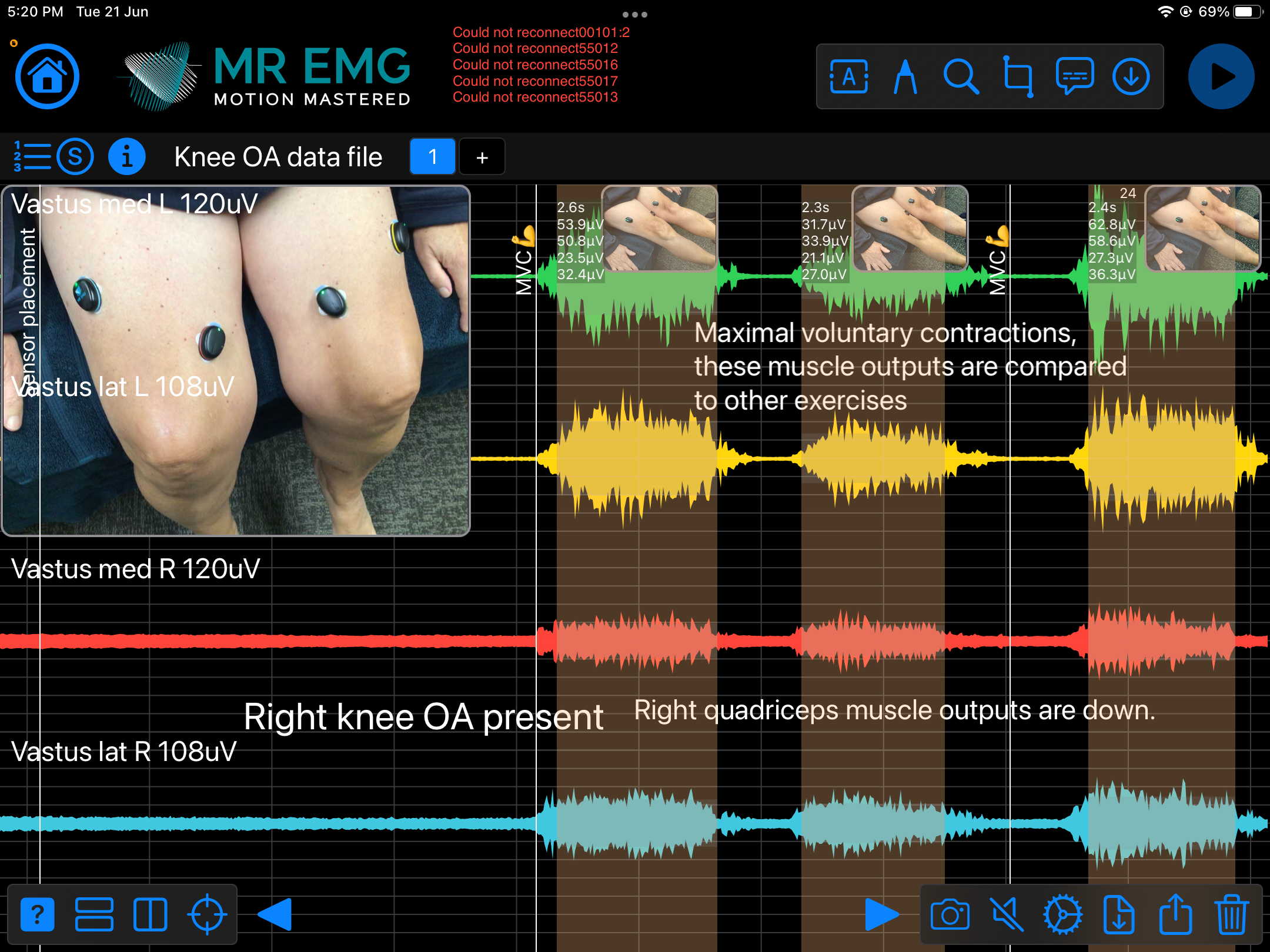
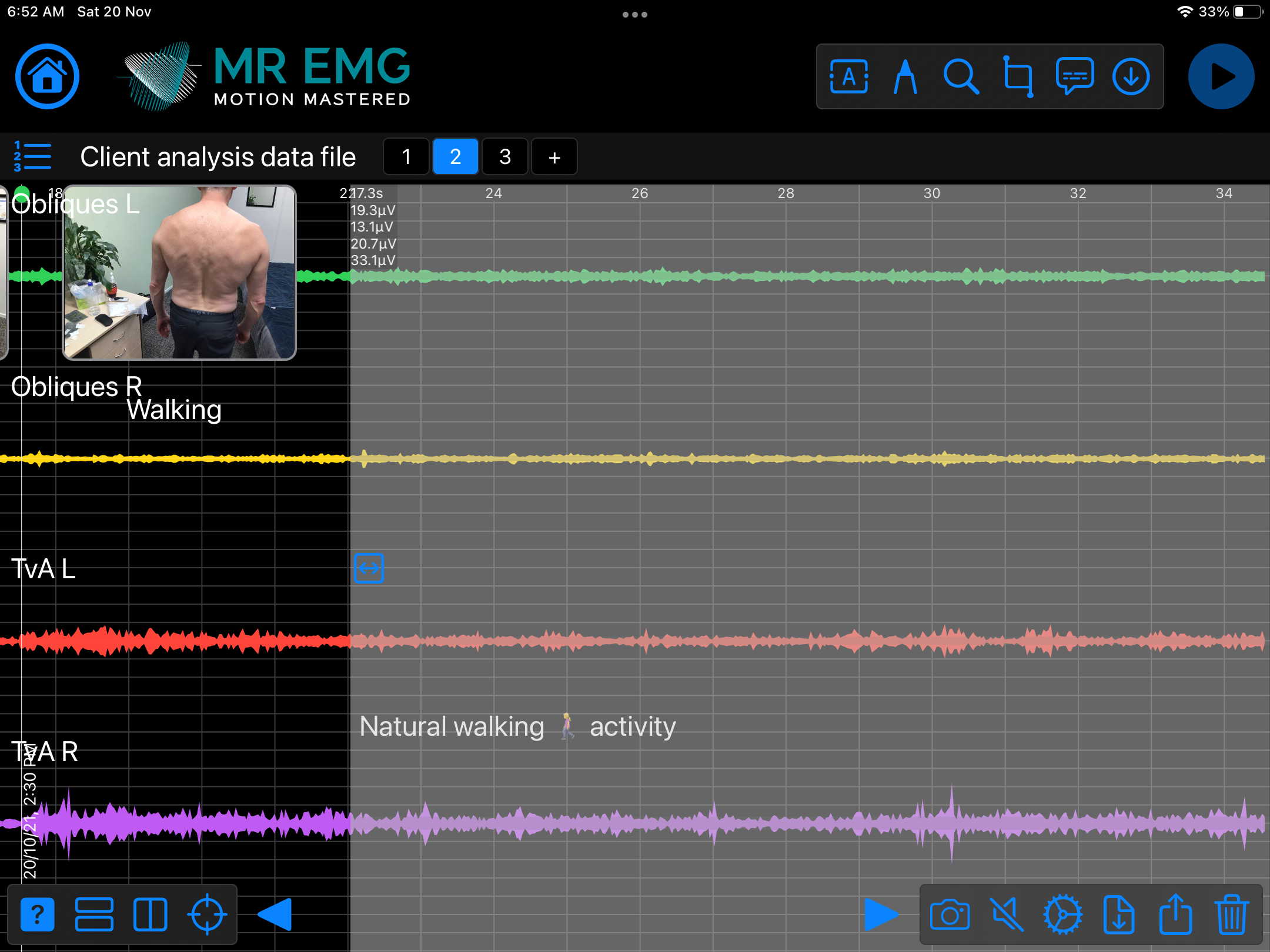
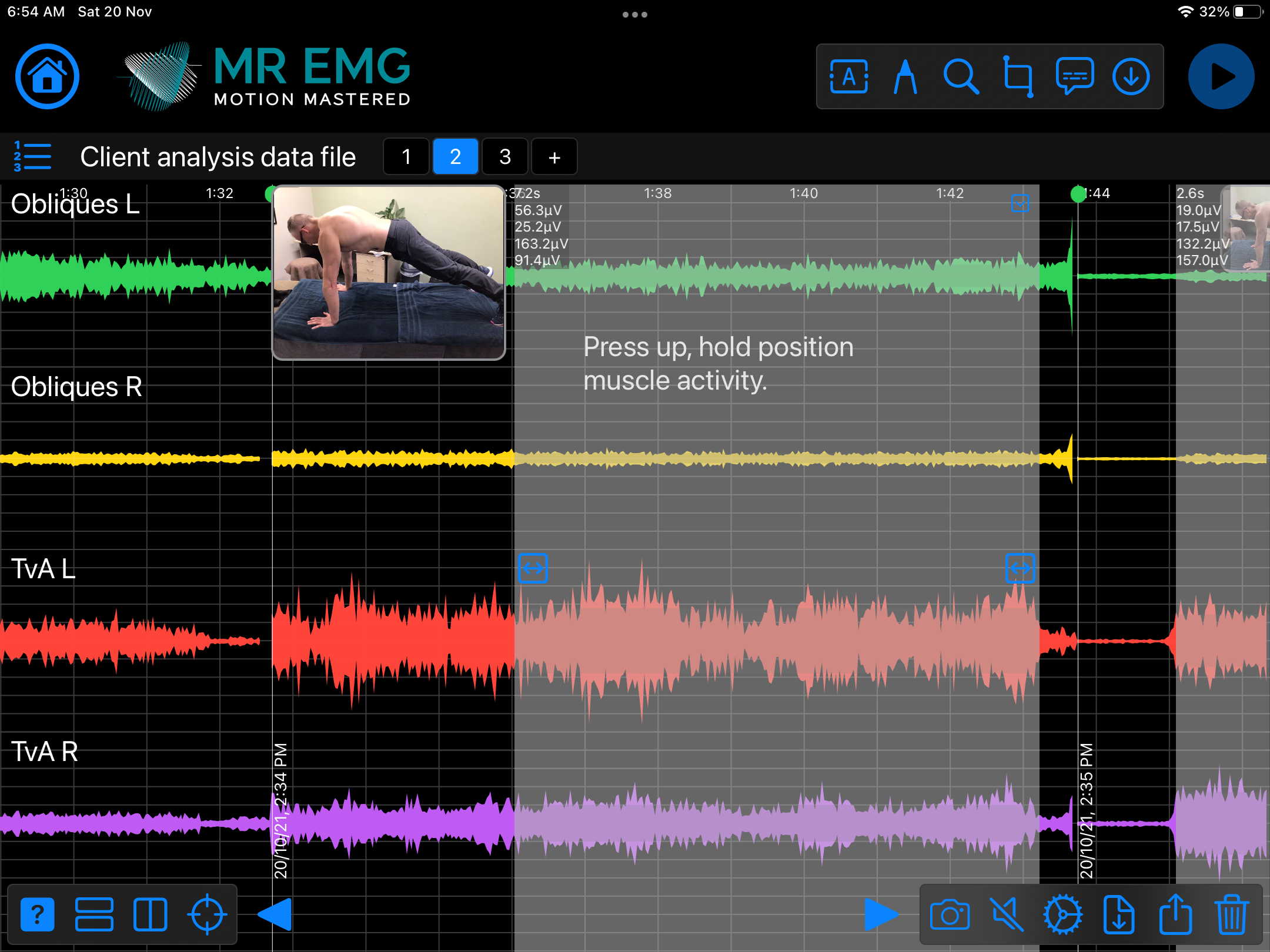
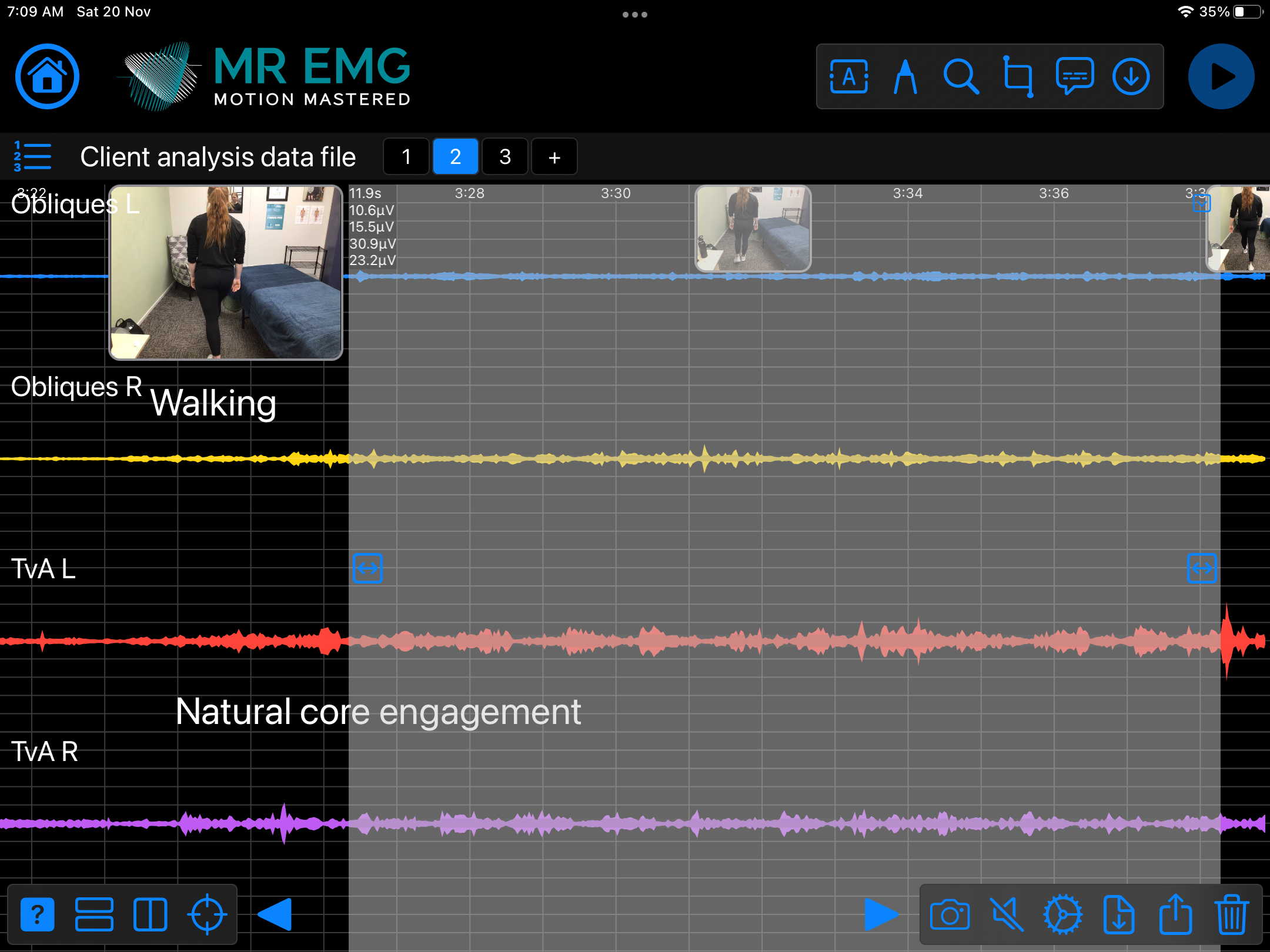
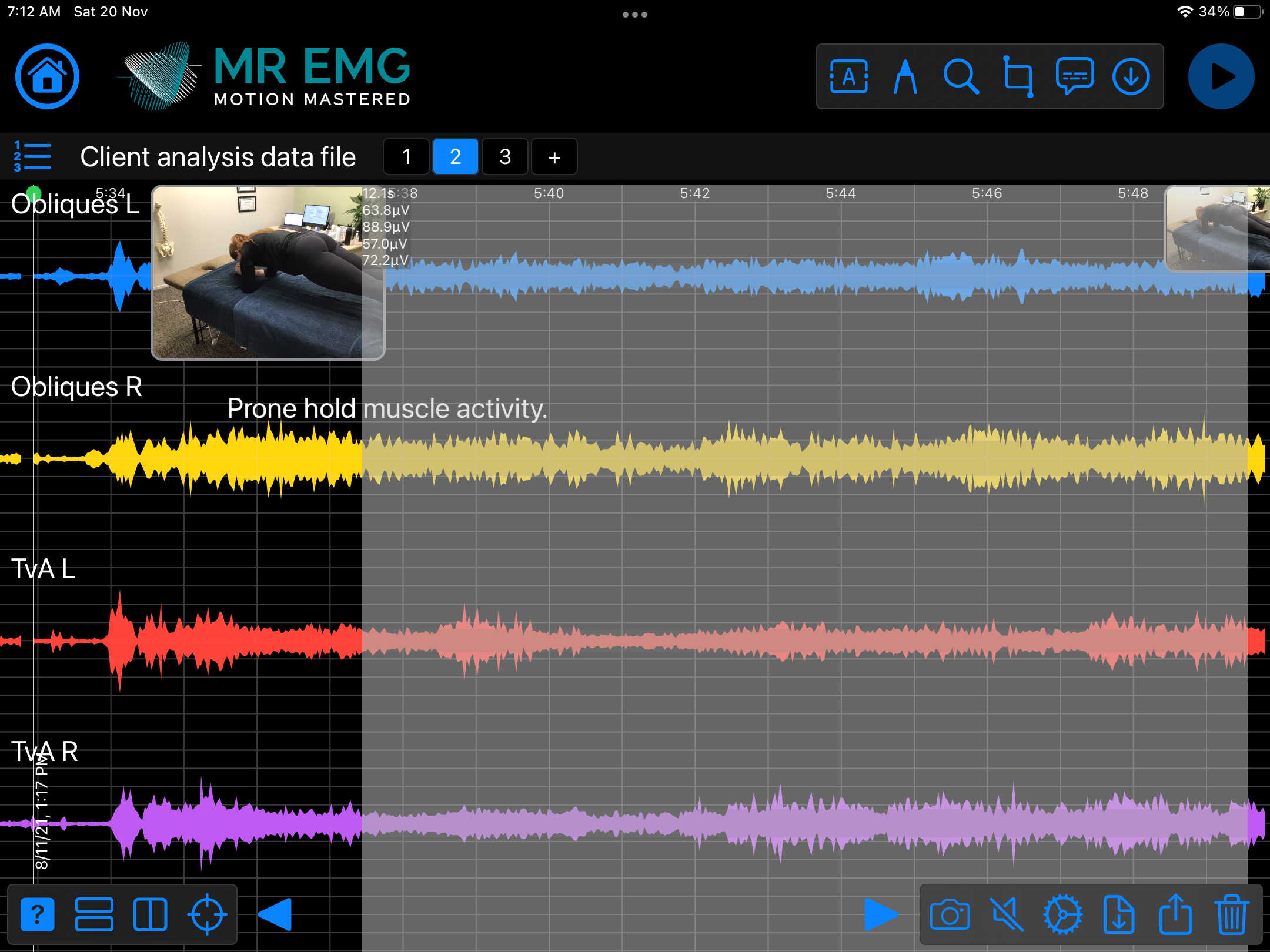
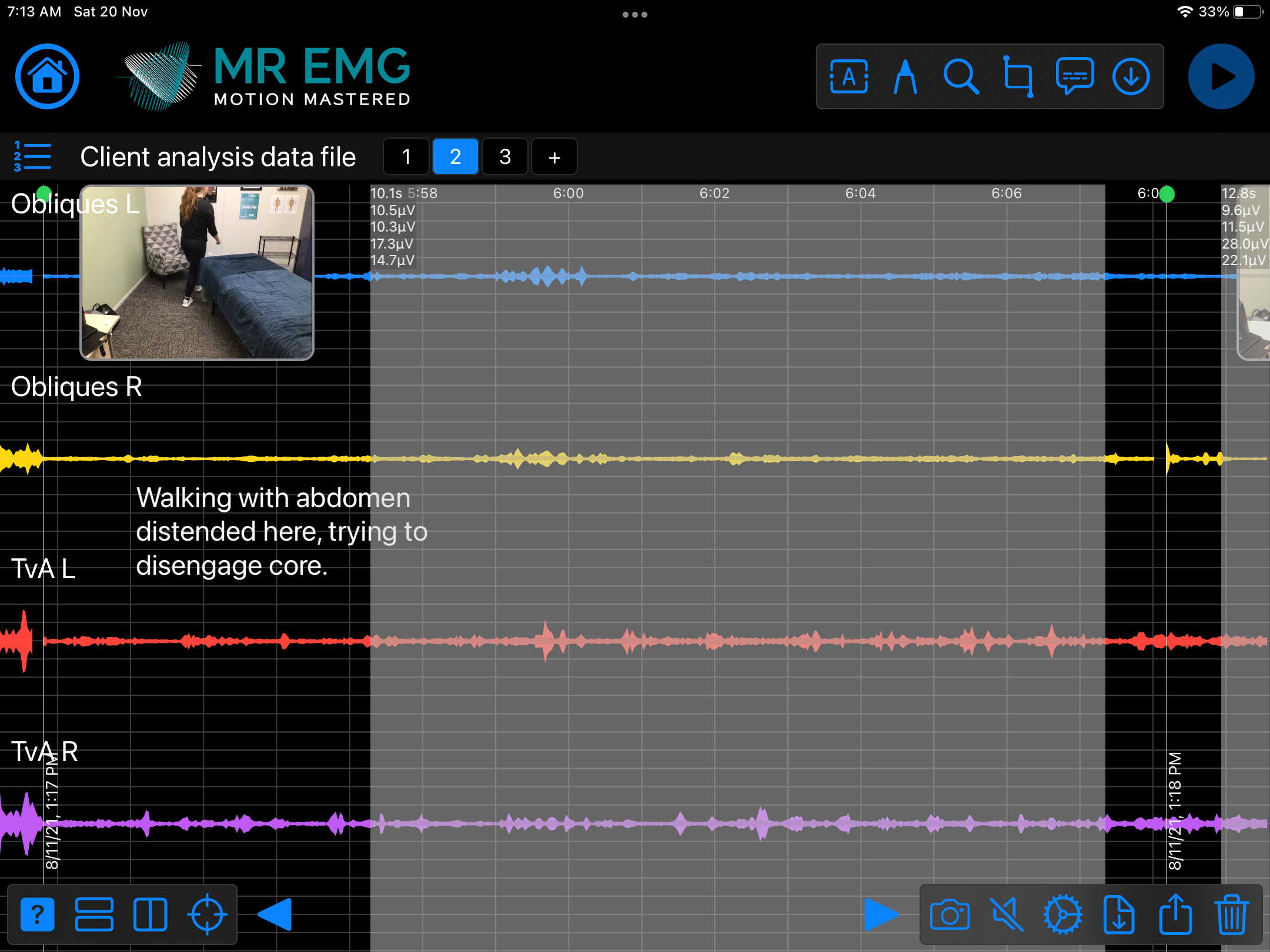
Here are examples of four muscle groups showing the correlation between neural drive and muscle excitation. As the weight being moved by the muscles increases so does the contraction force generated by the neural drive.
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
Consider testing the Erector Spinae muscles for
Consider testing the Erector spinae thoracic for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for
Consider testing these muscles for
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
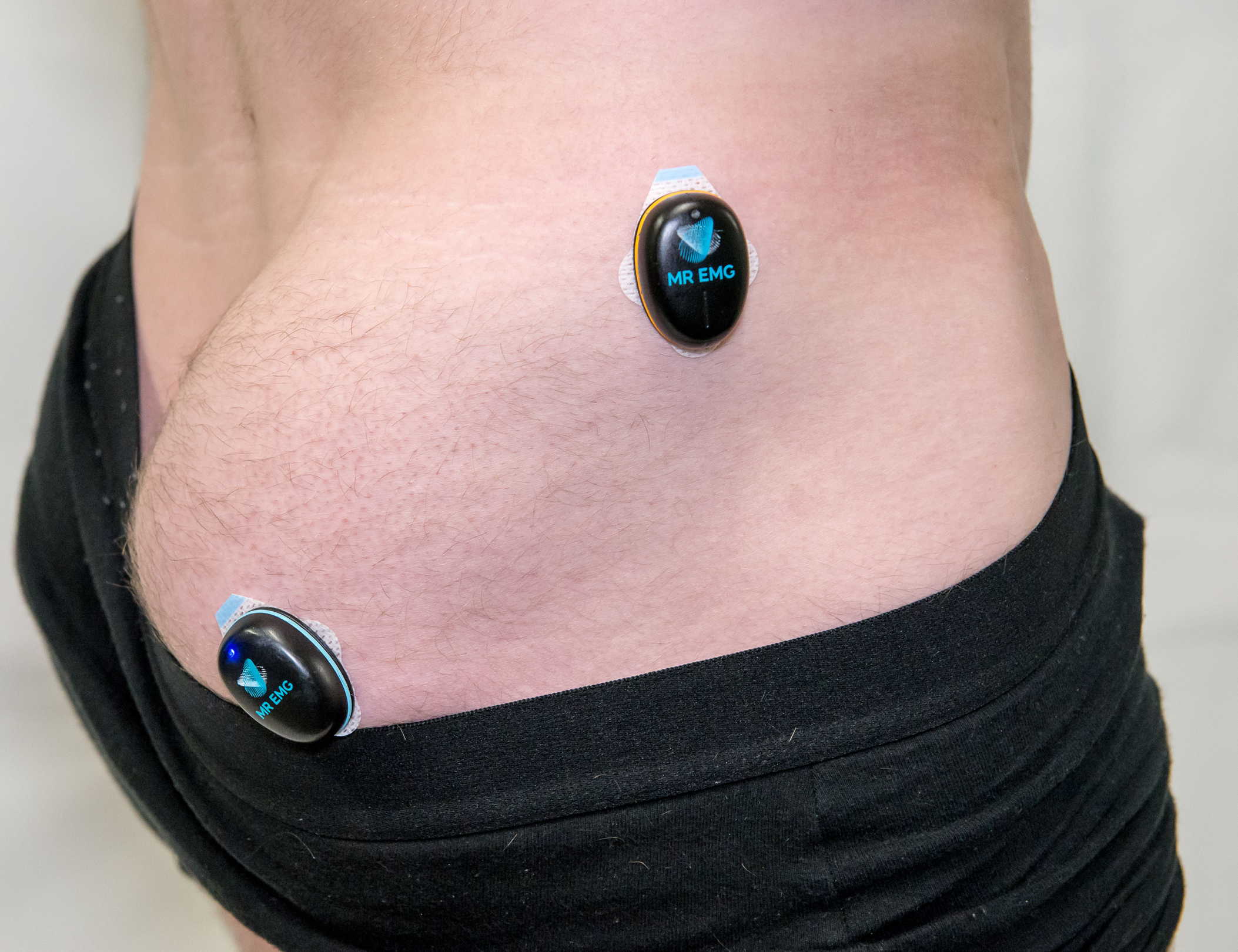
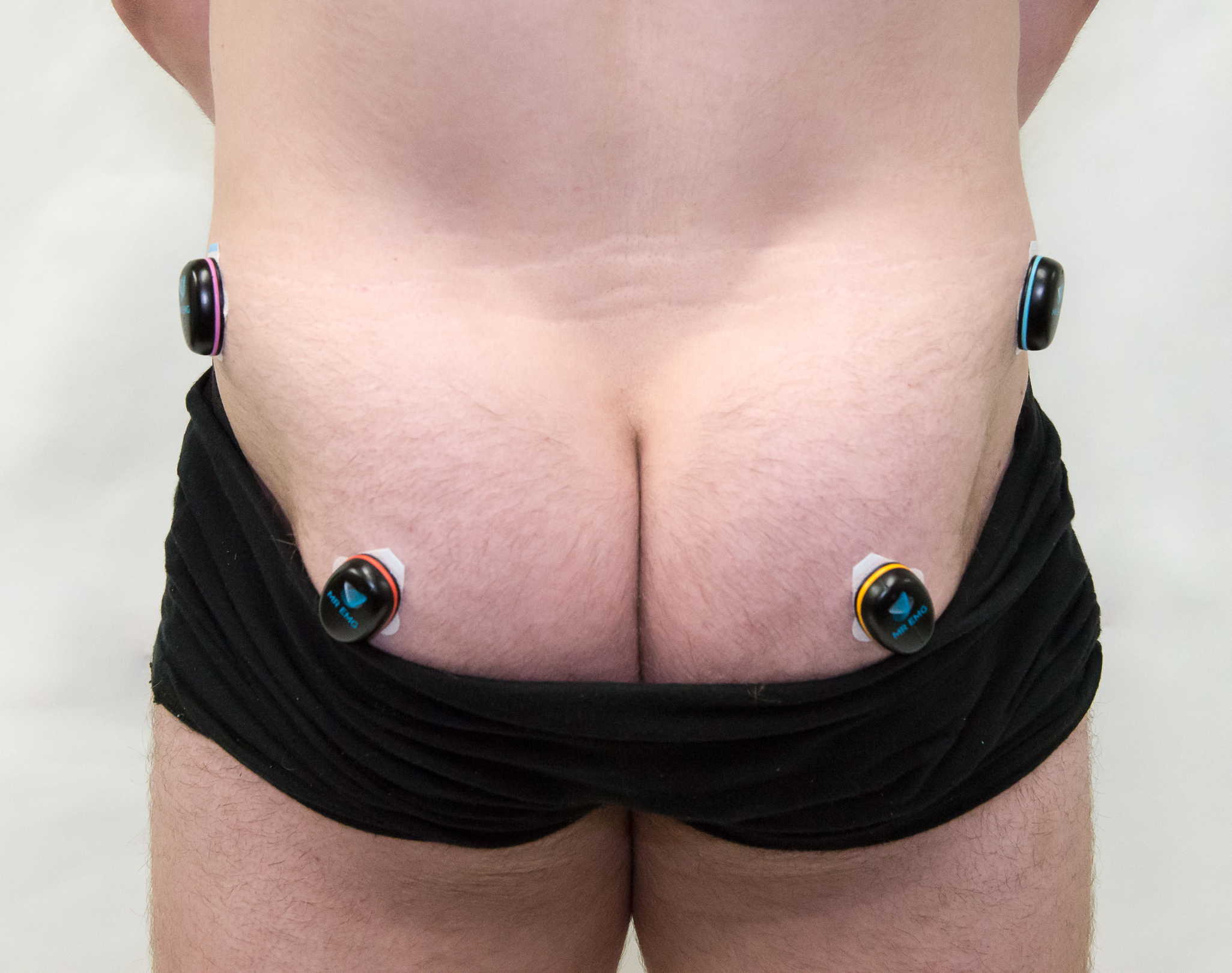
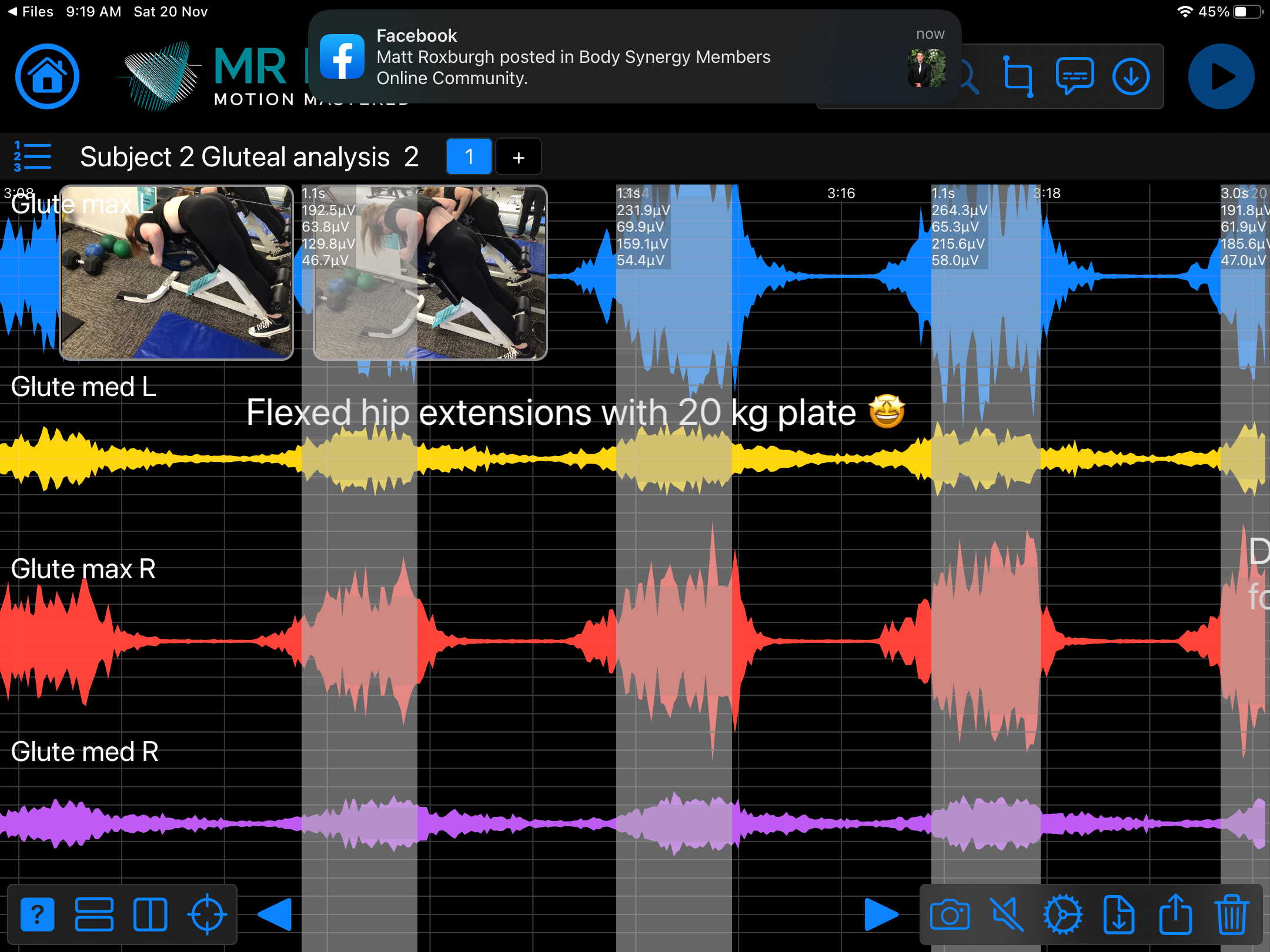
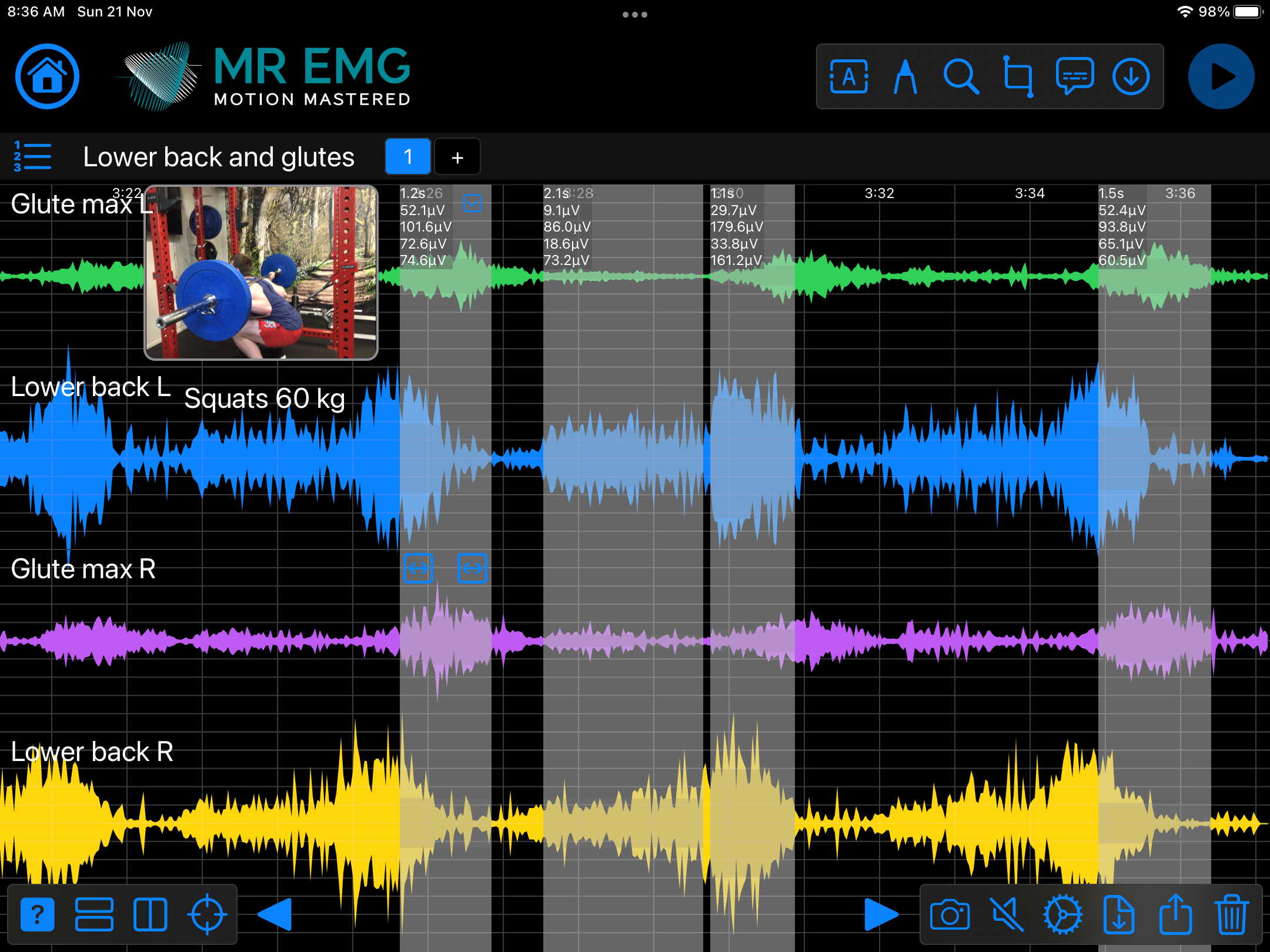

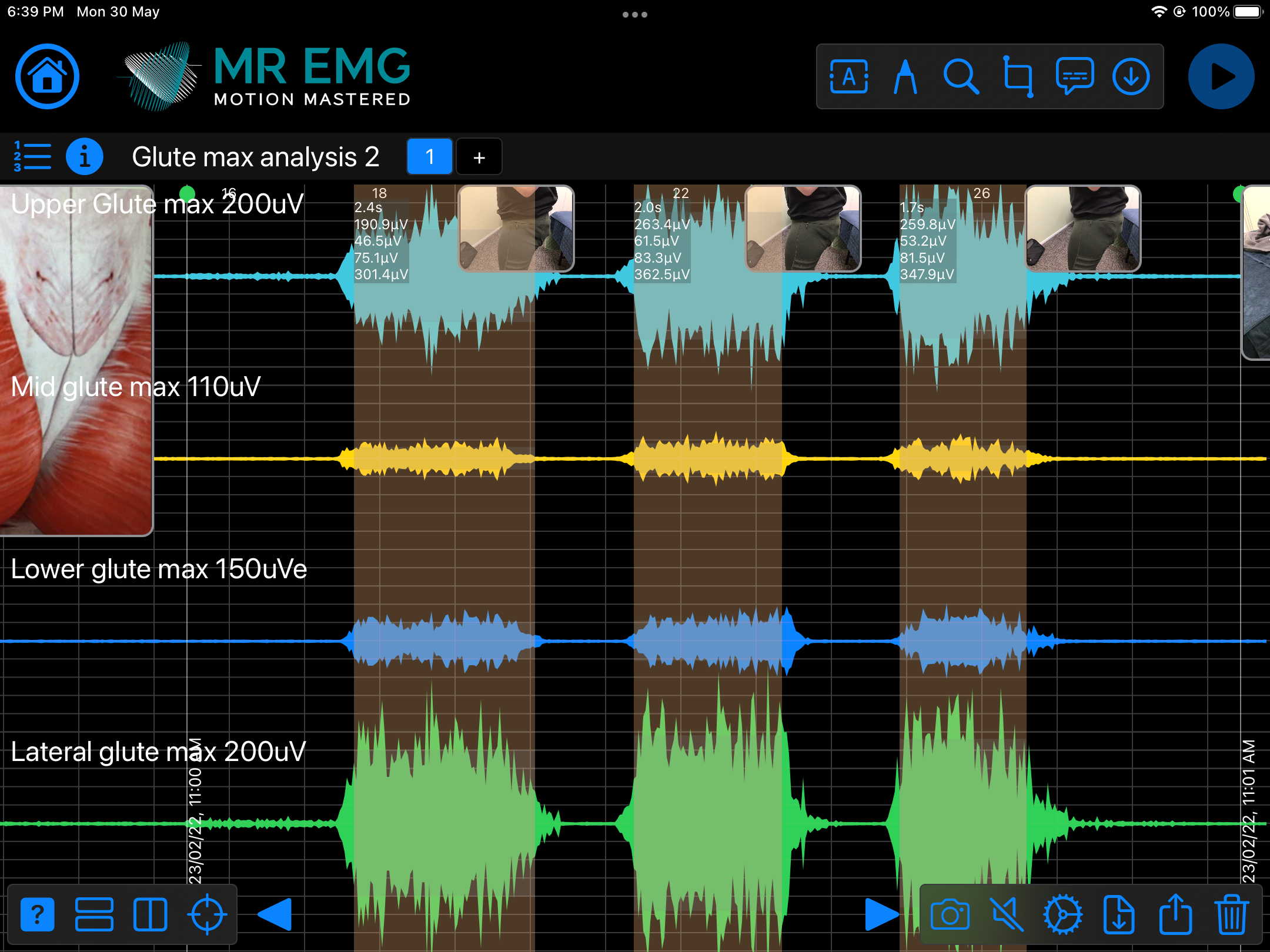
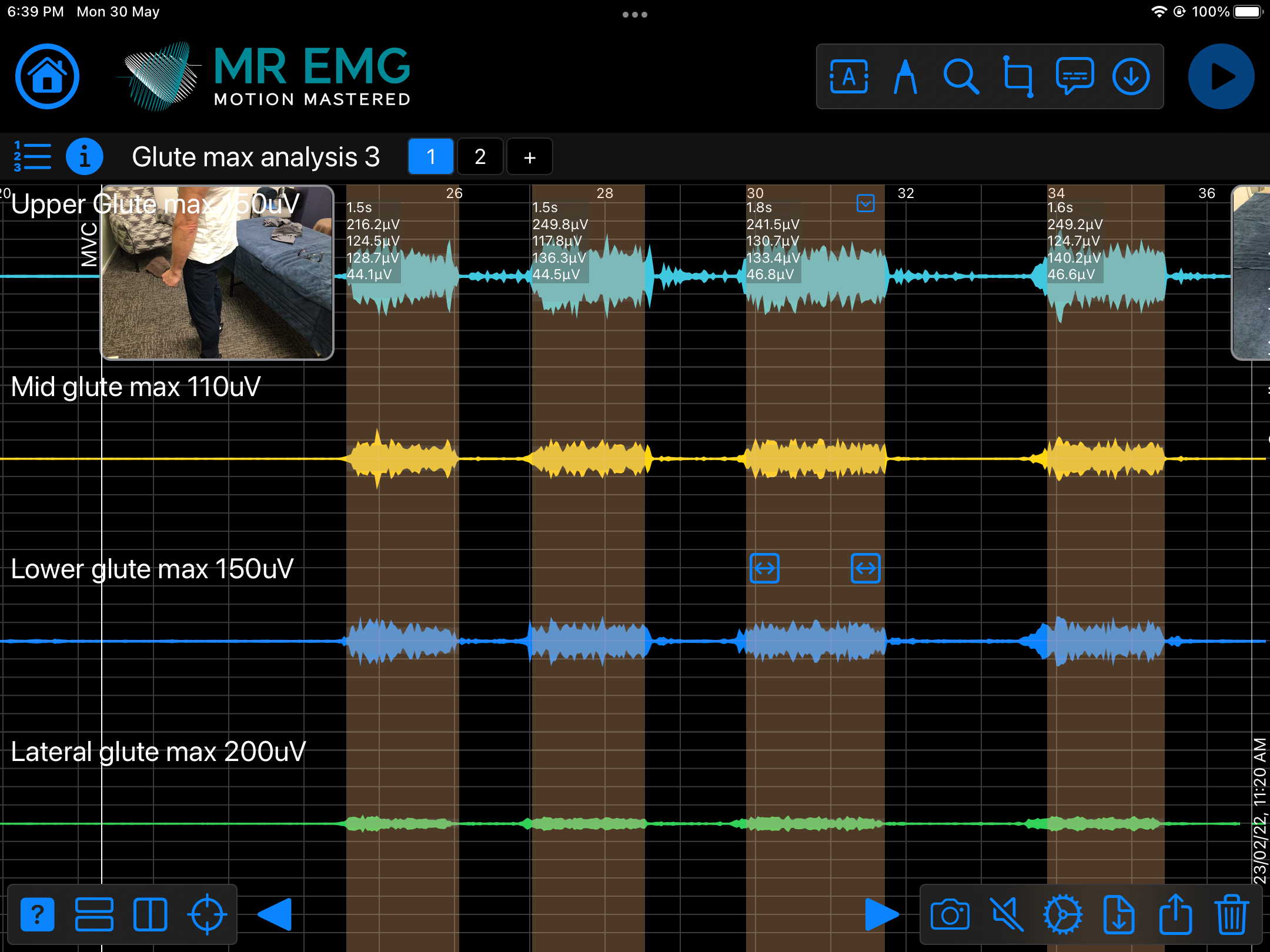
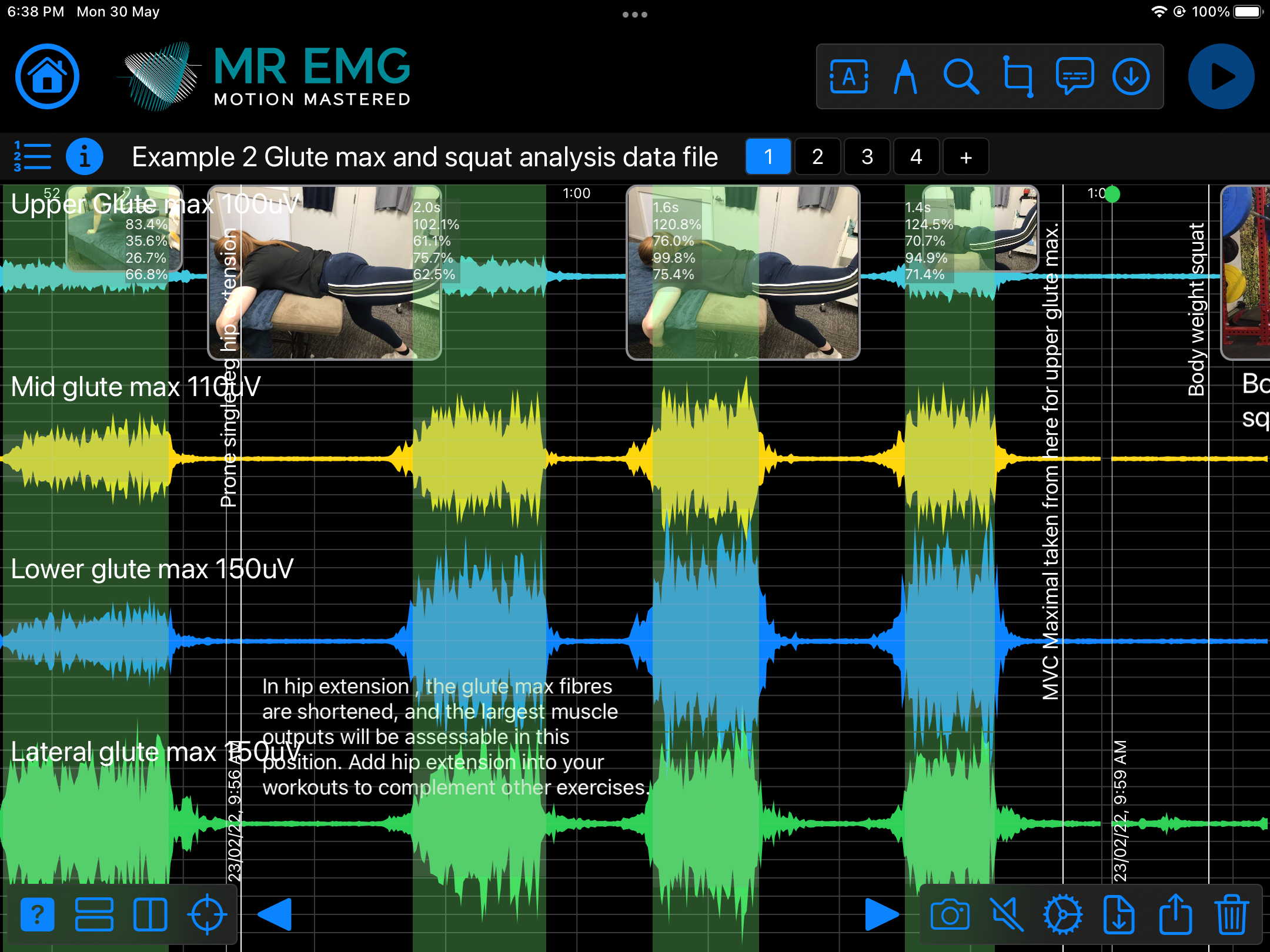
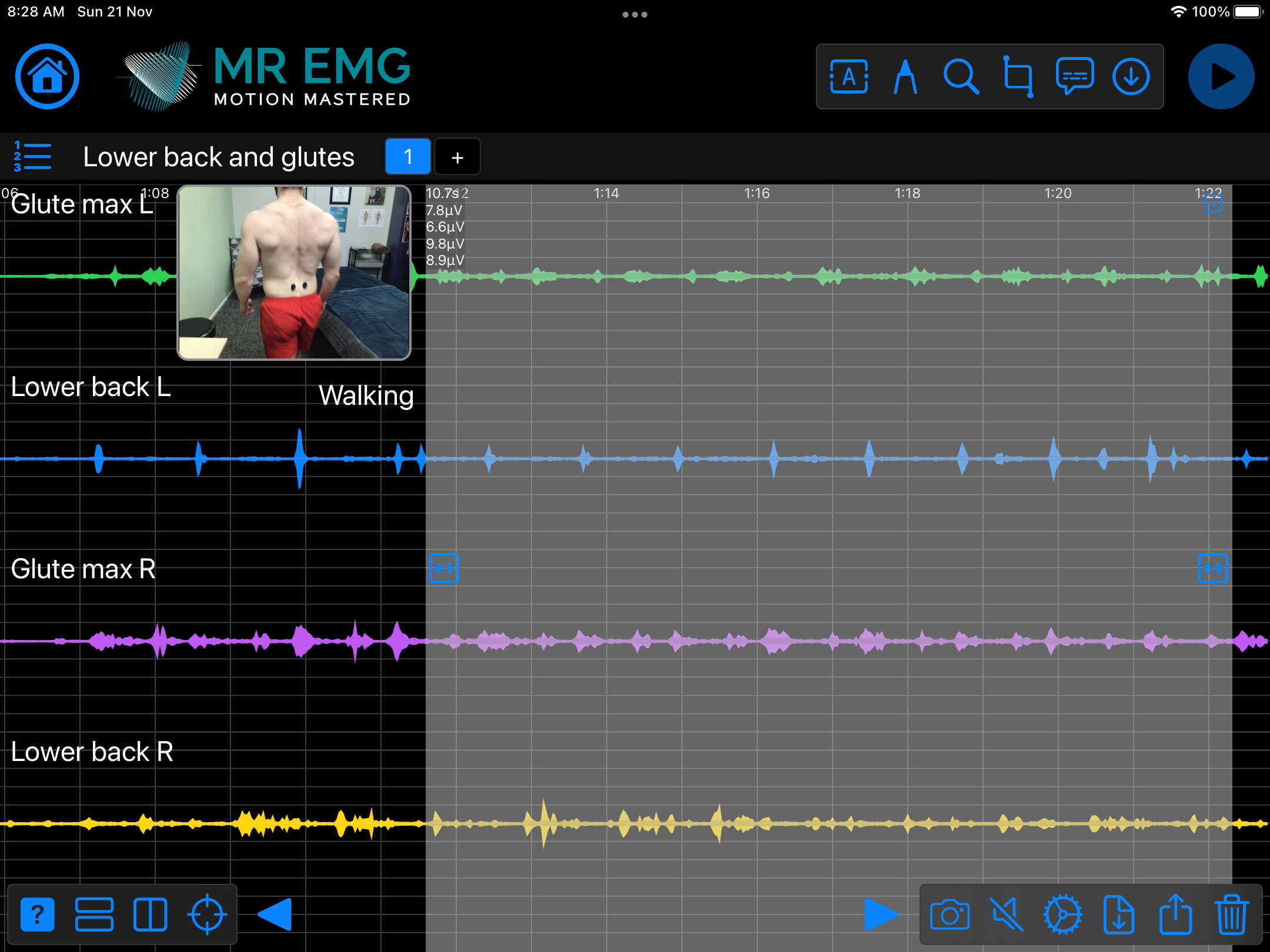
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
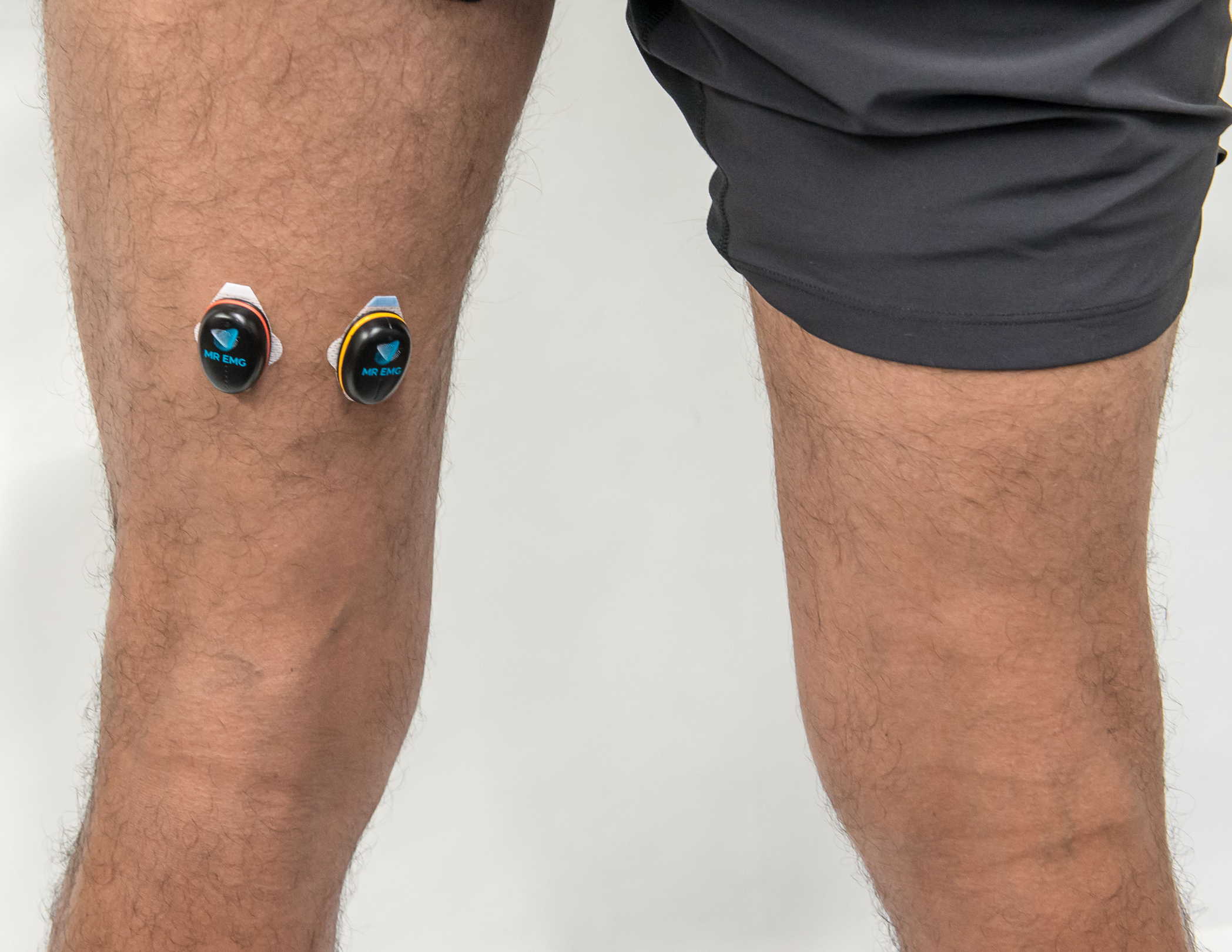
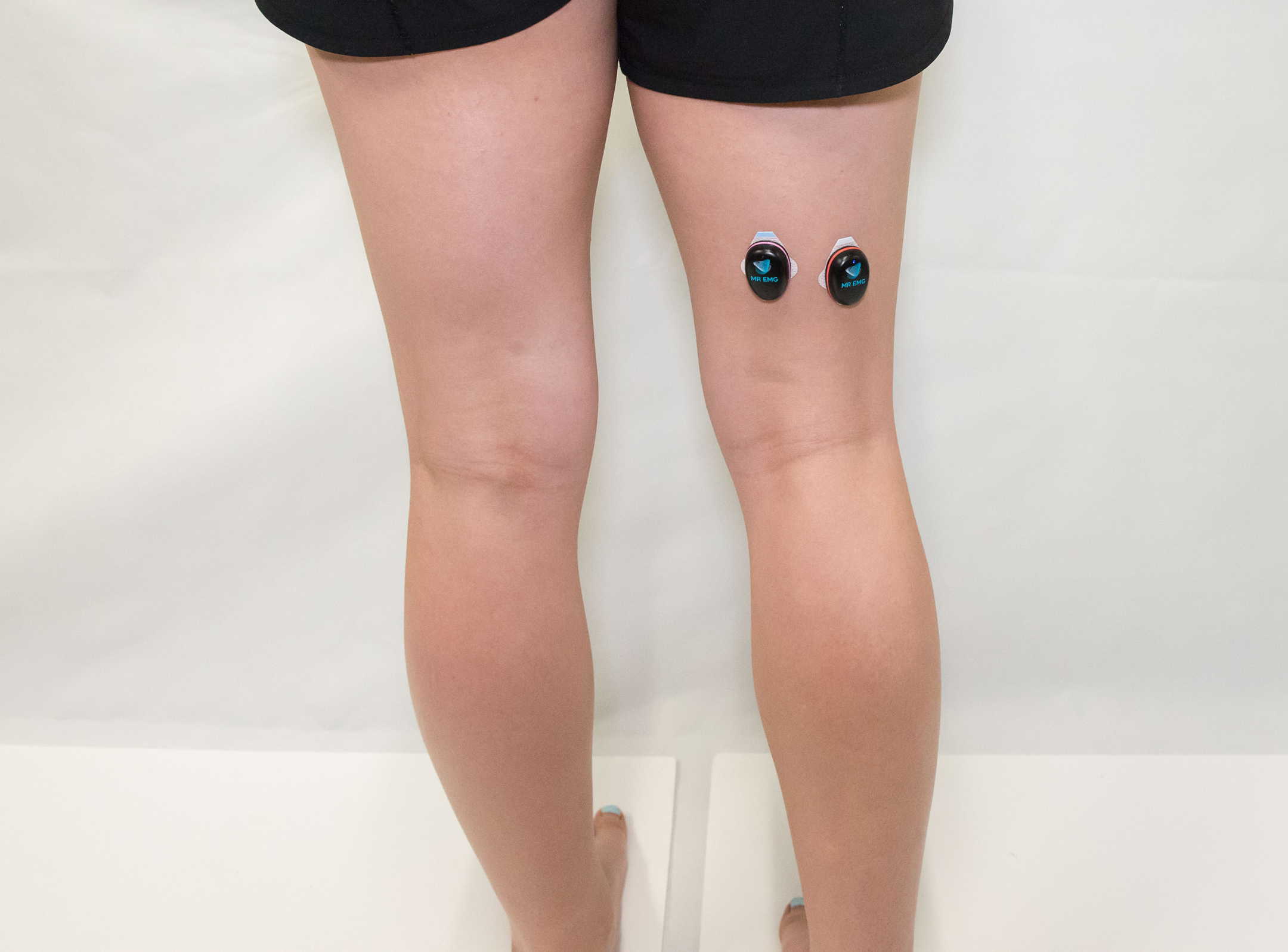
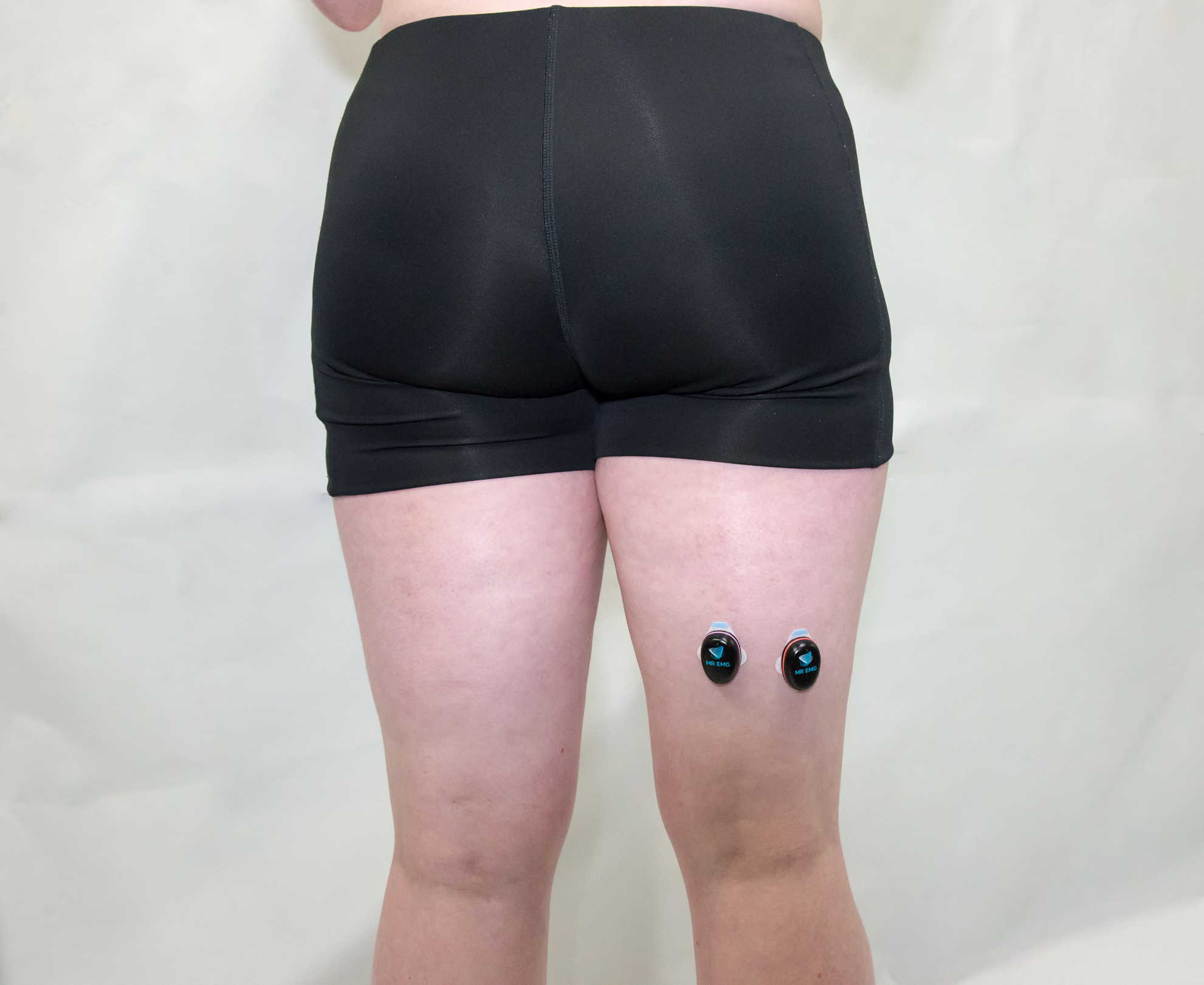
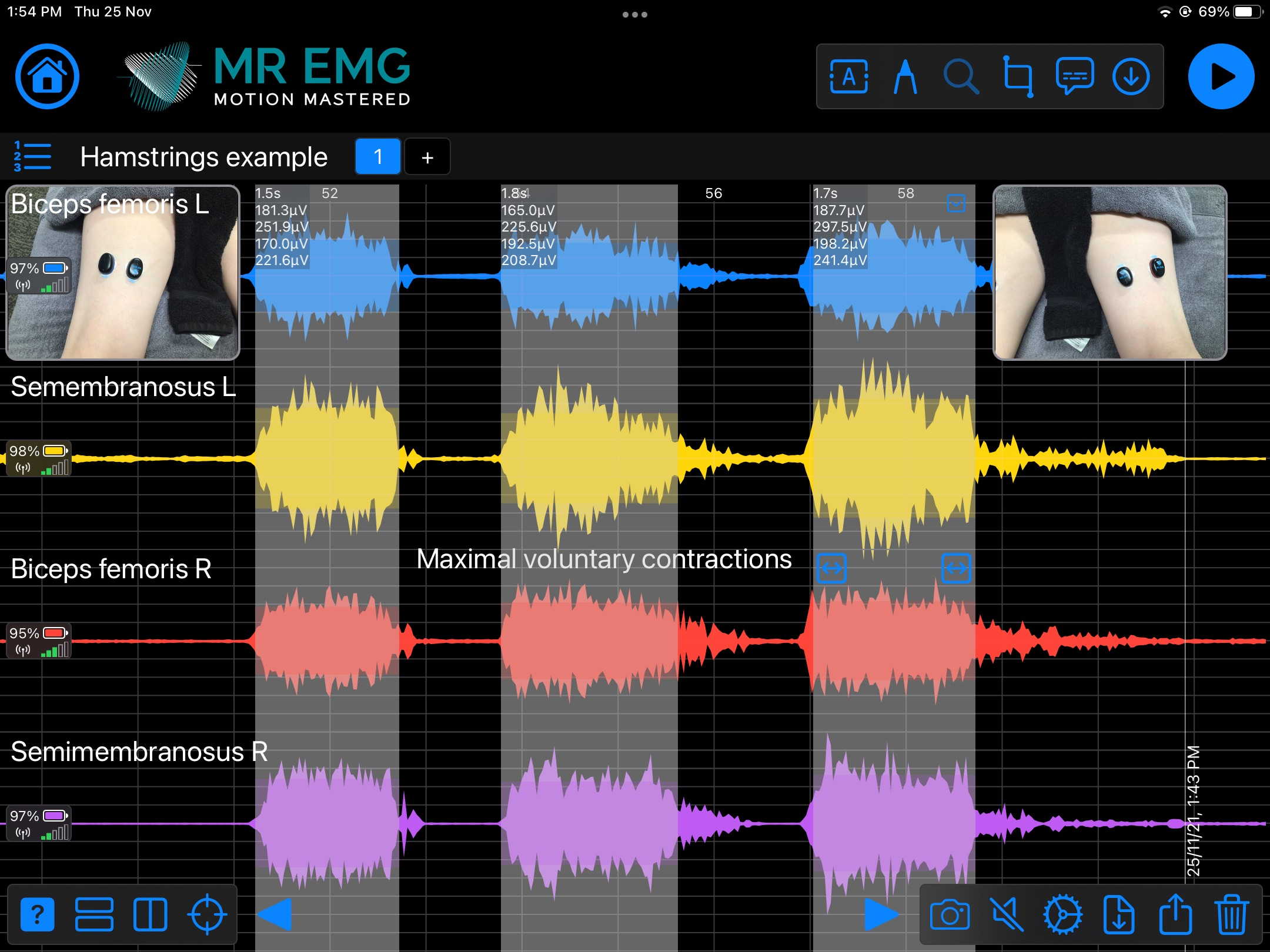
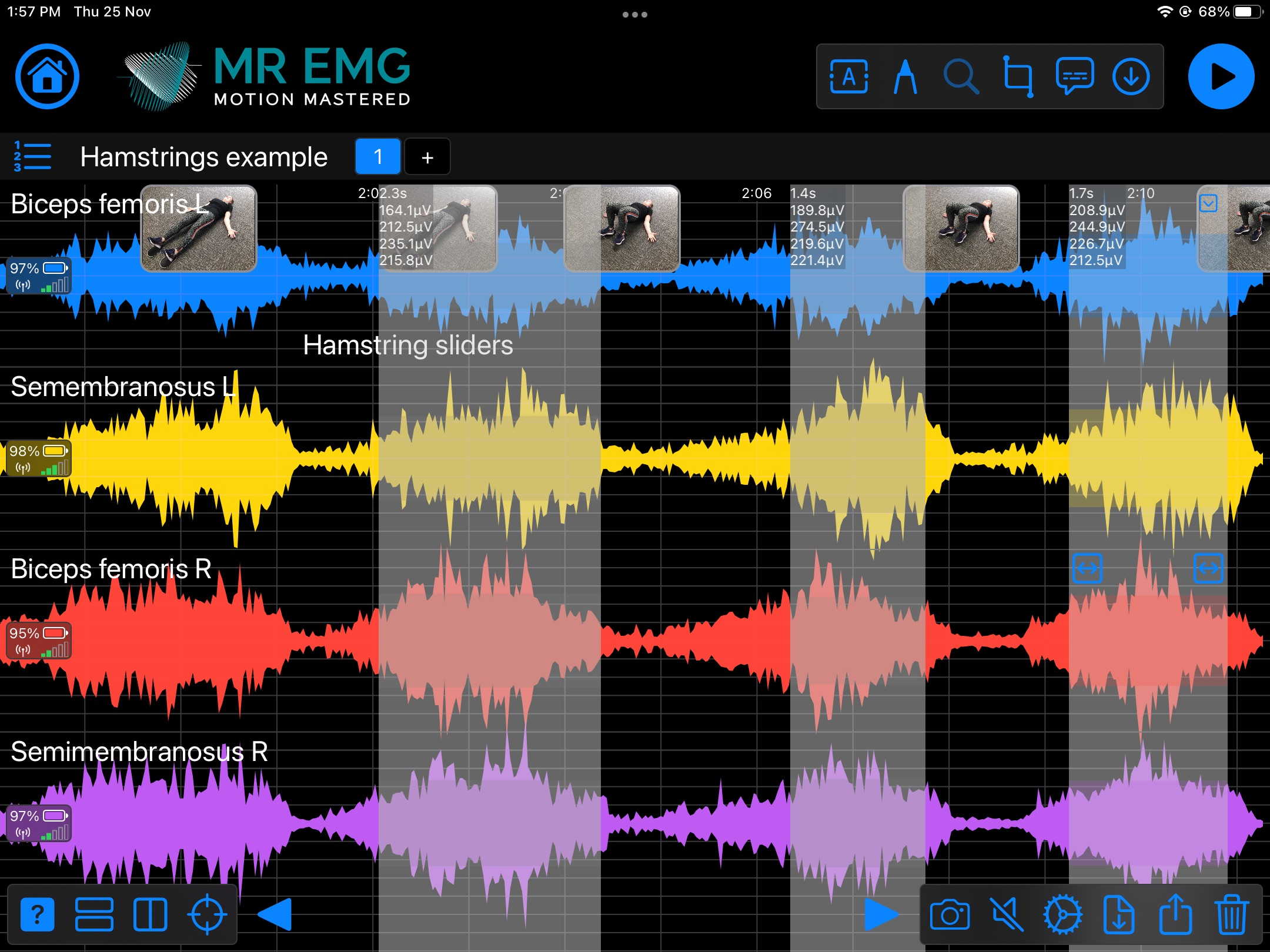
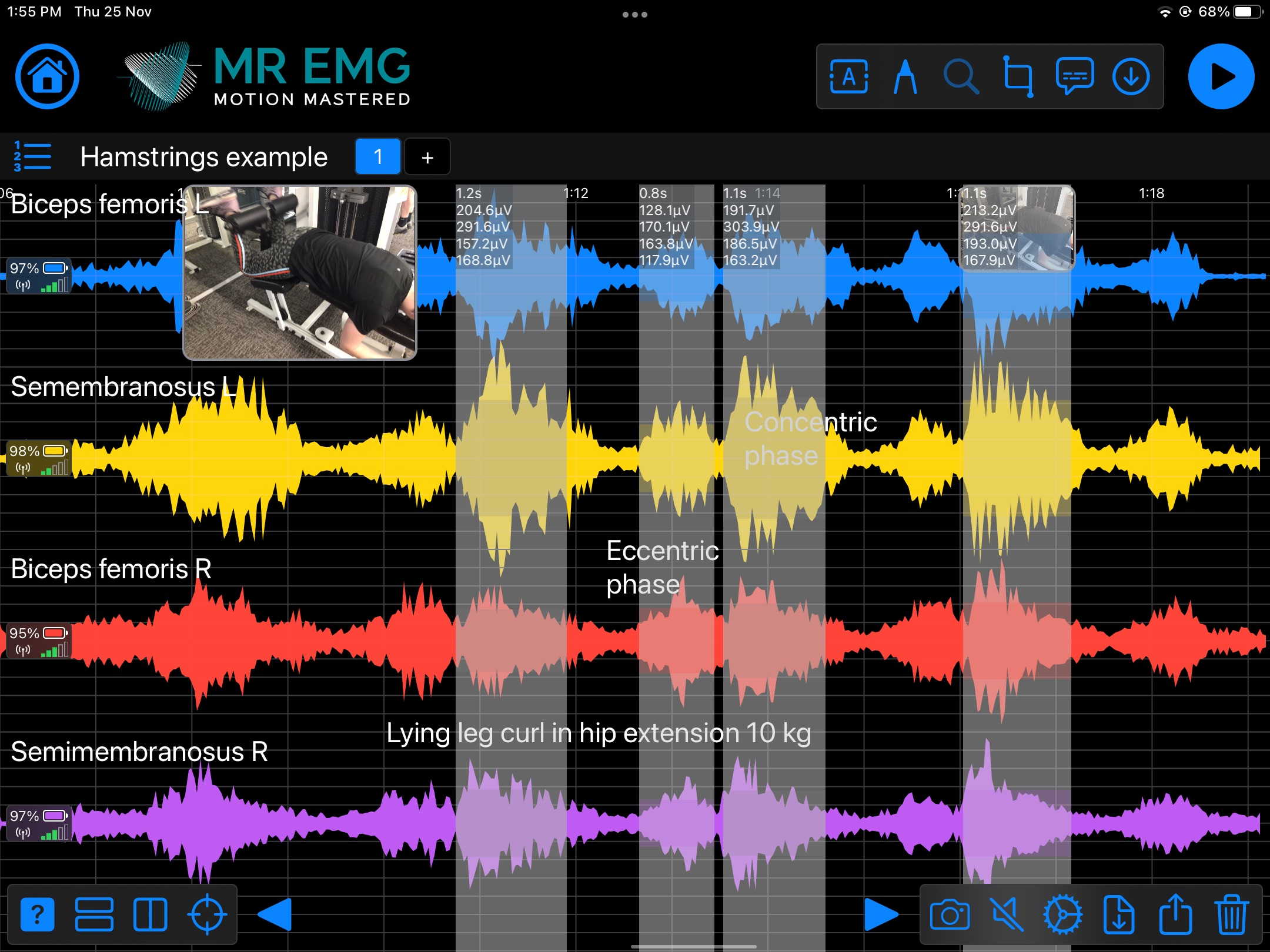
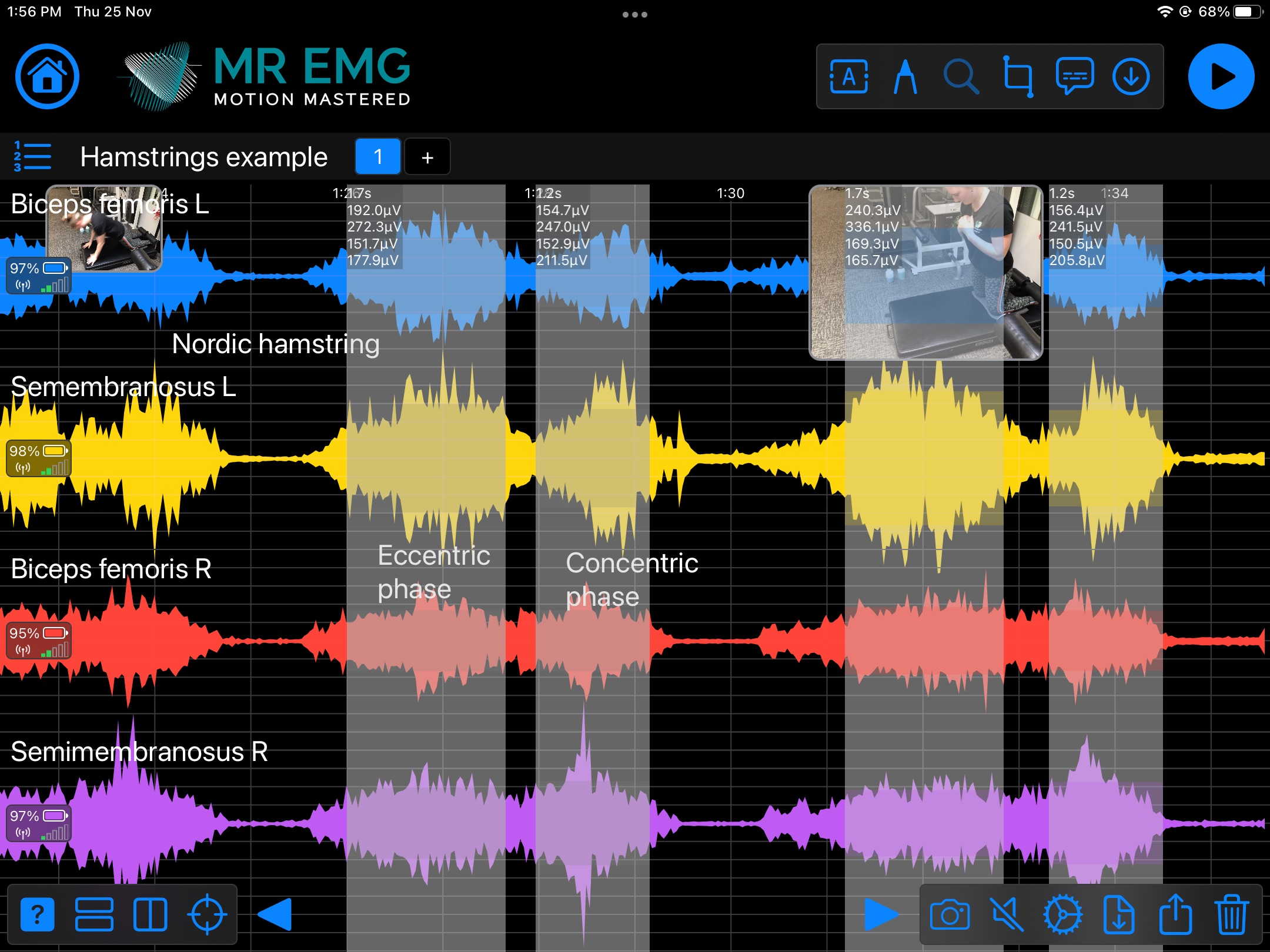
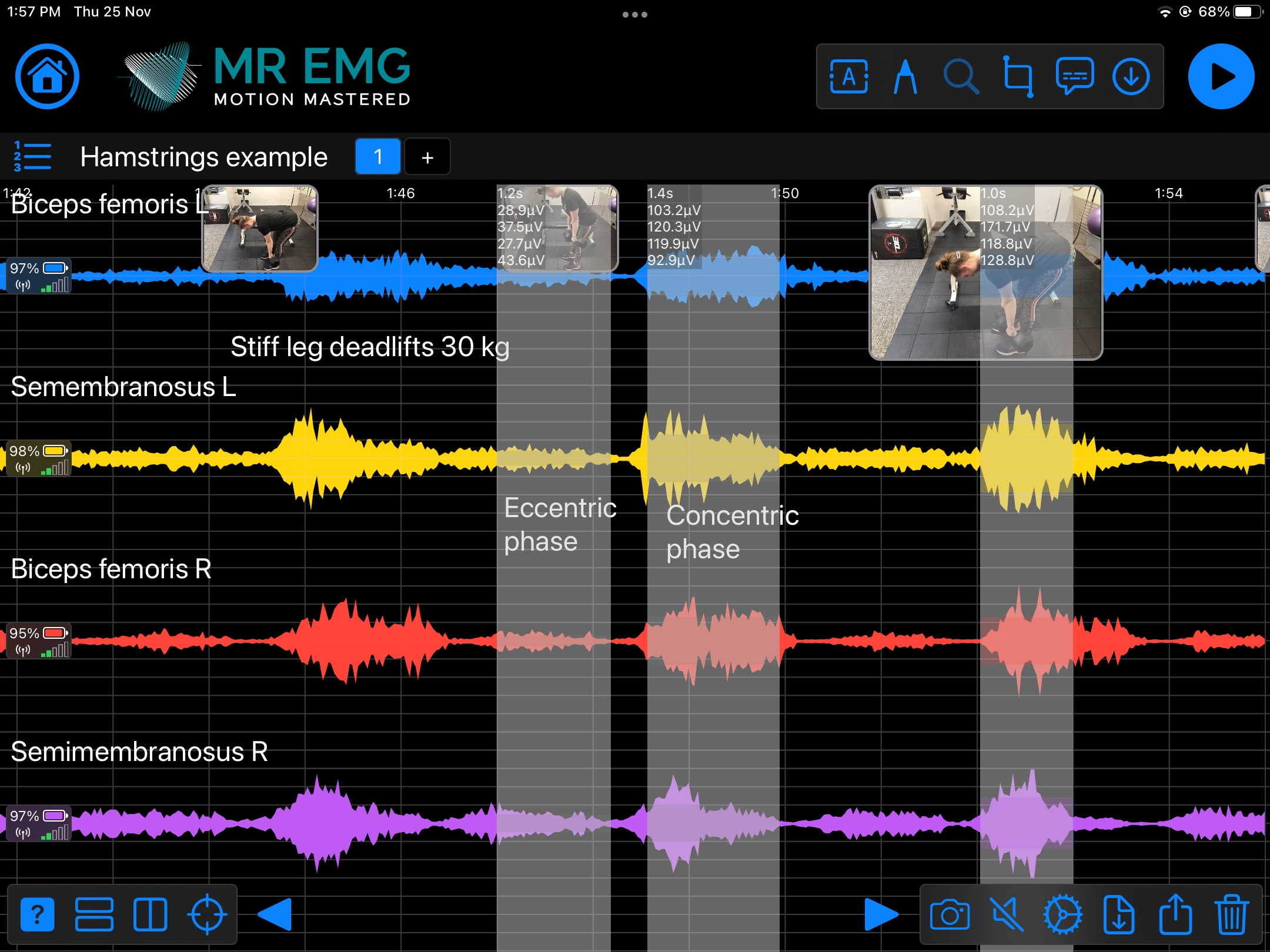
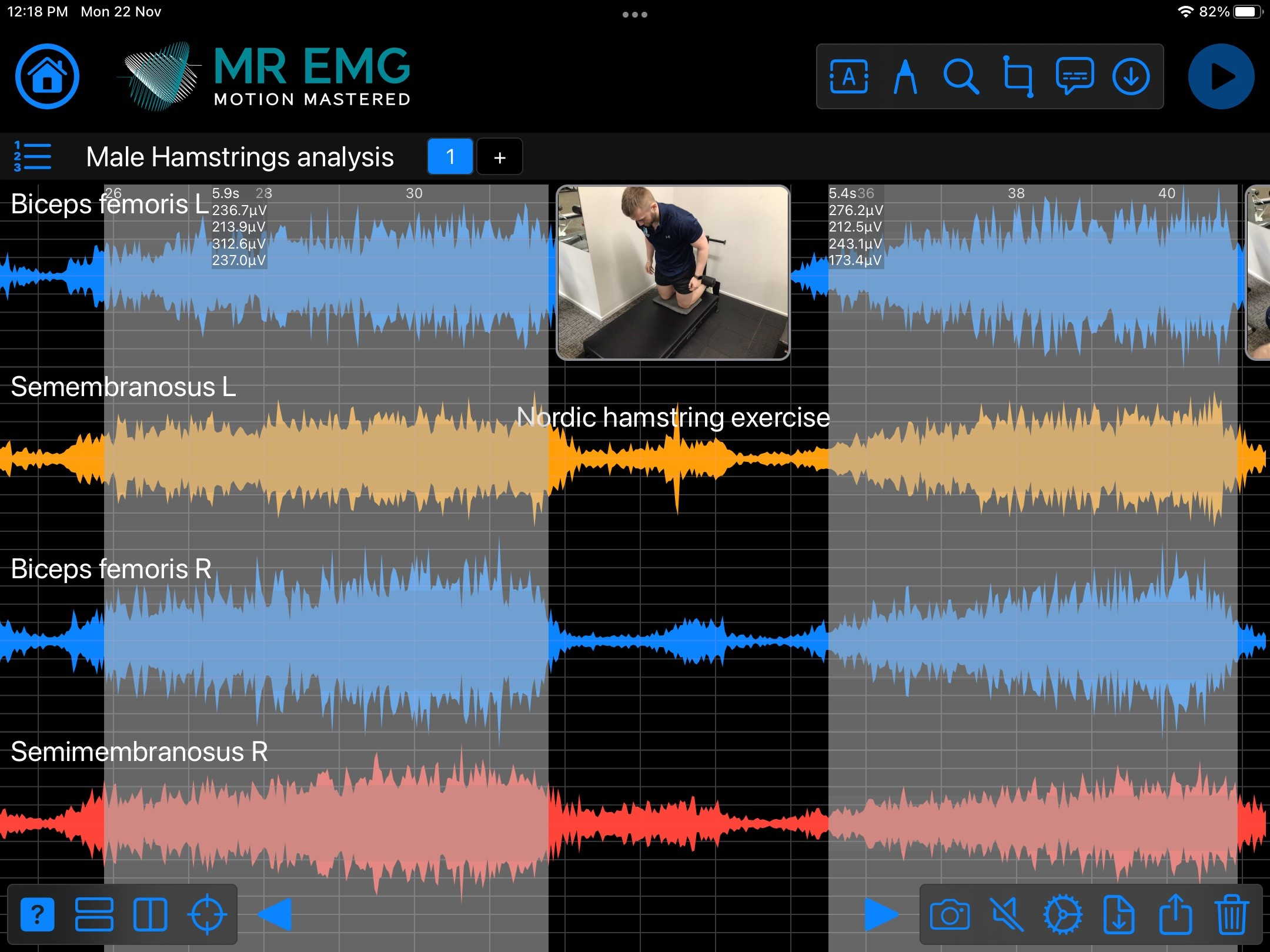
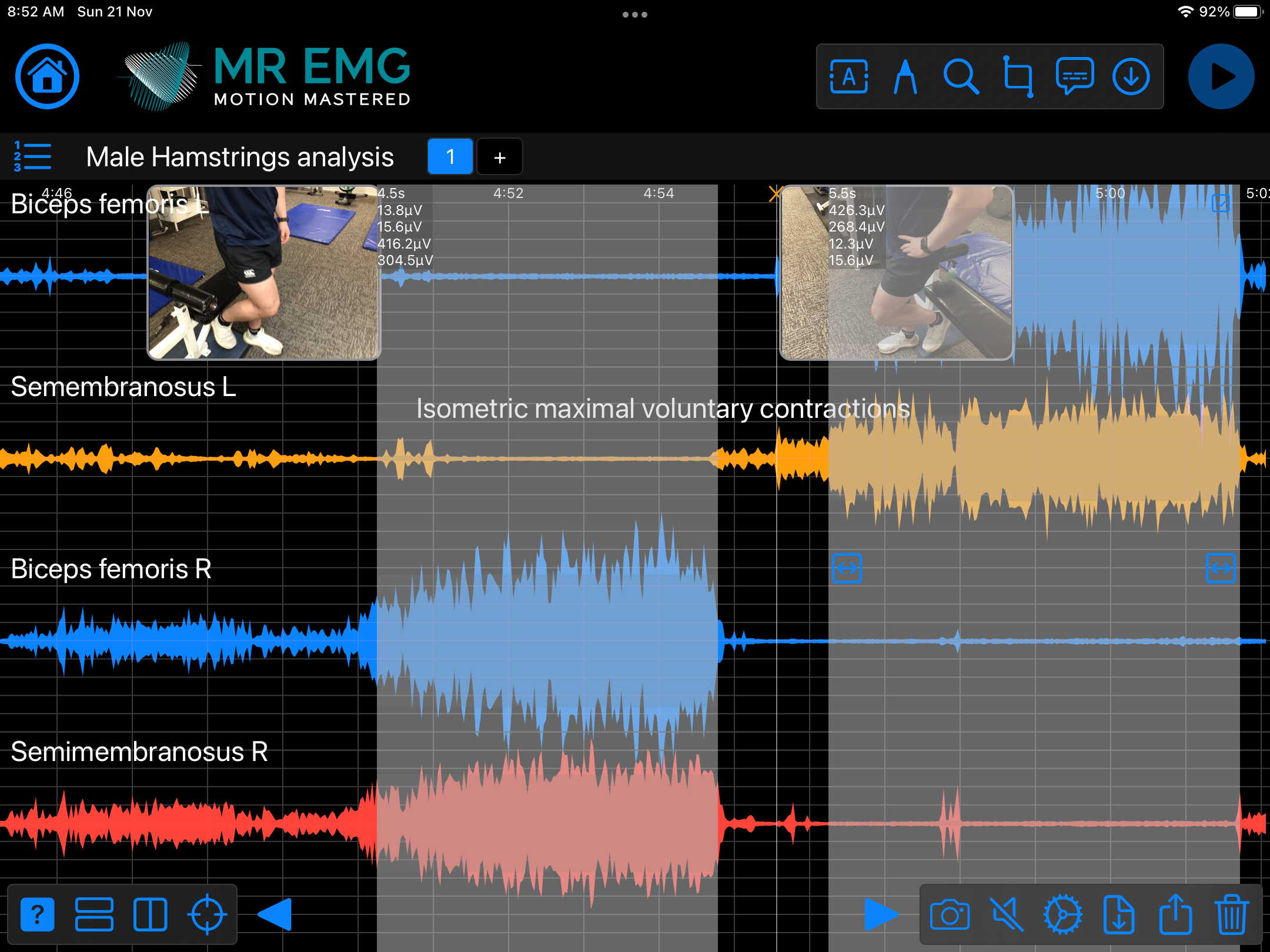
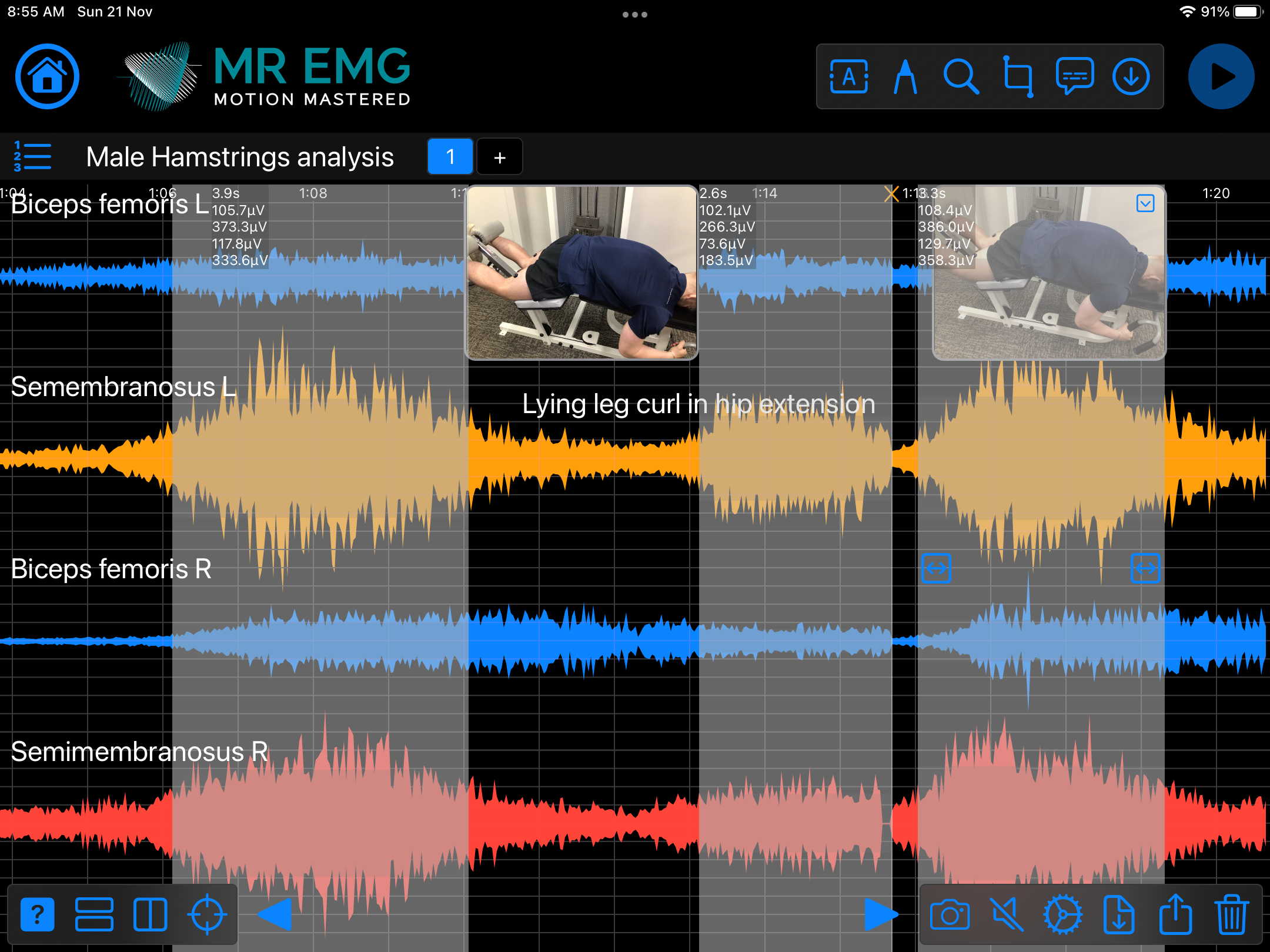
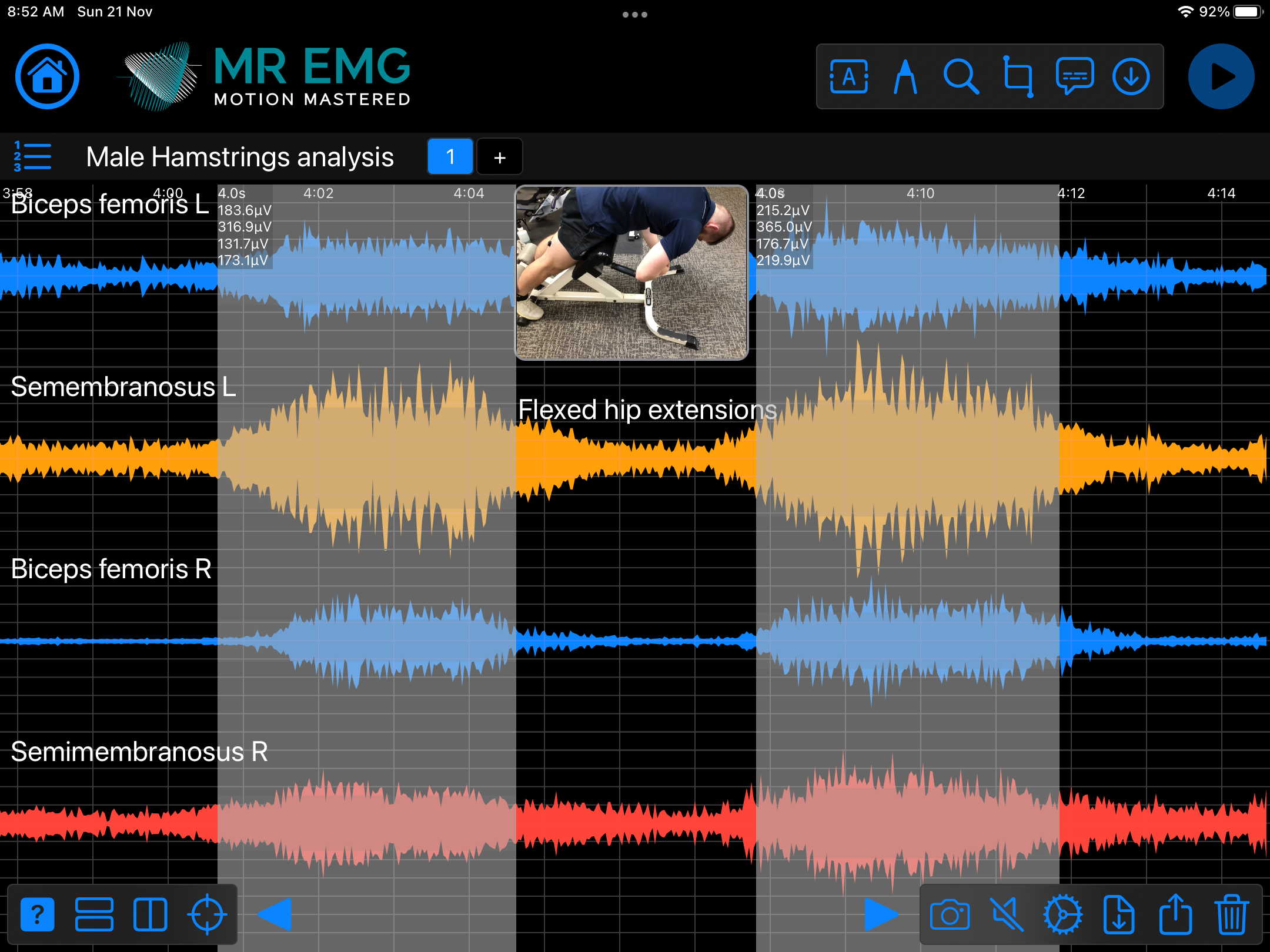
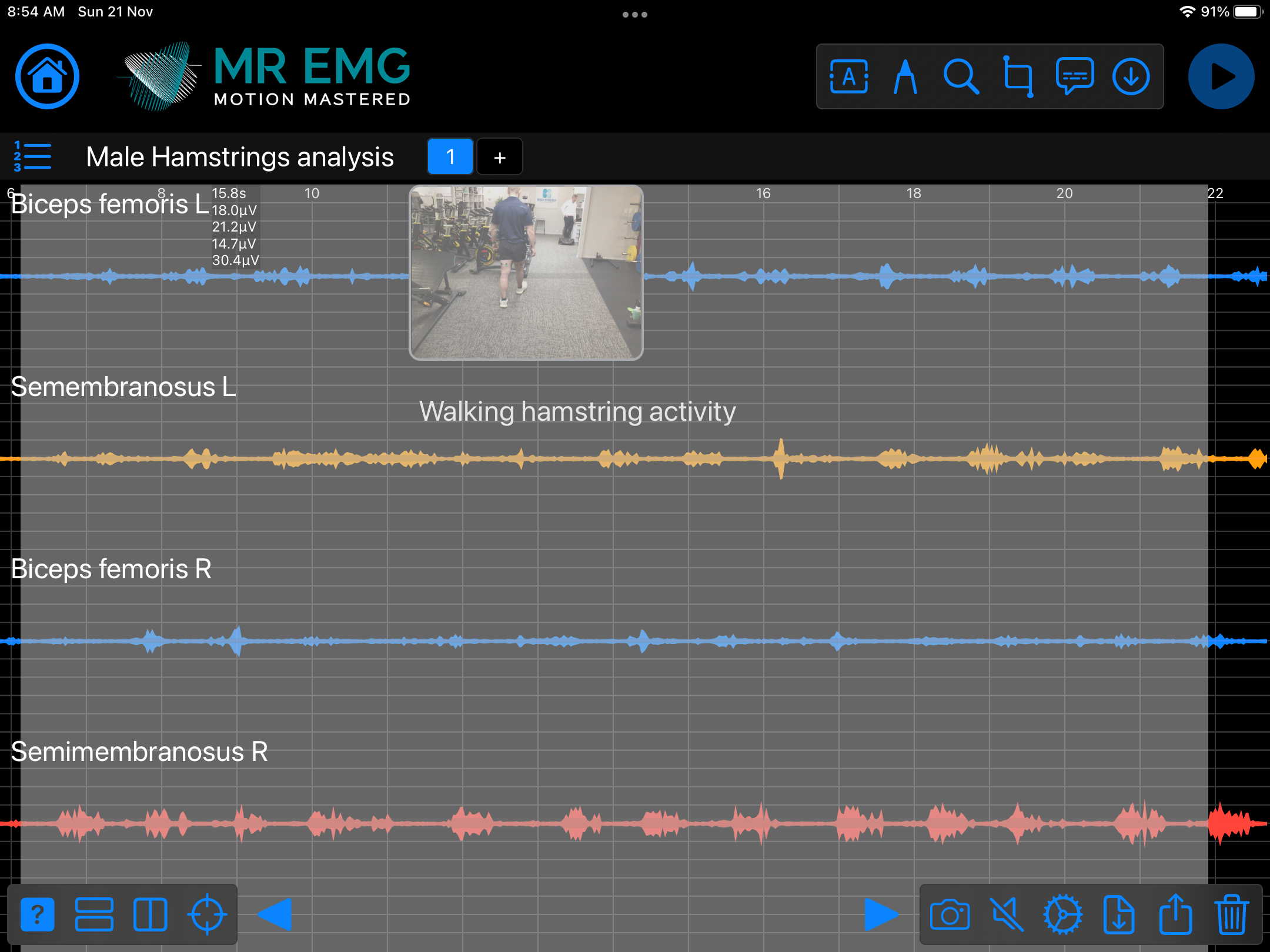
Consider testing these muscles for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
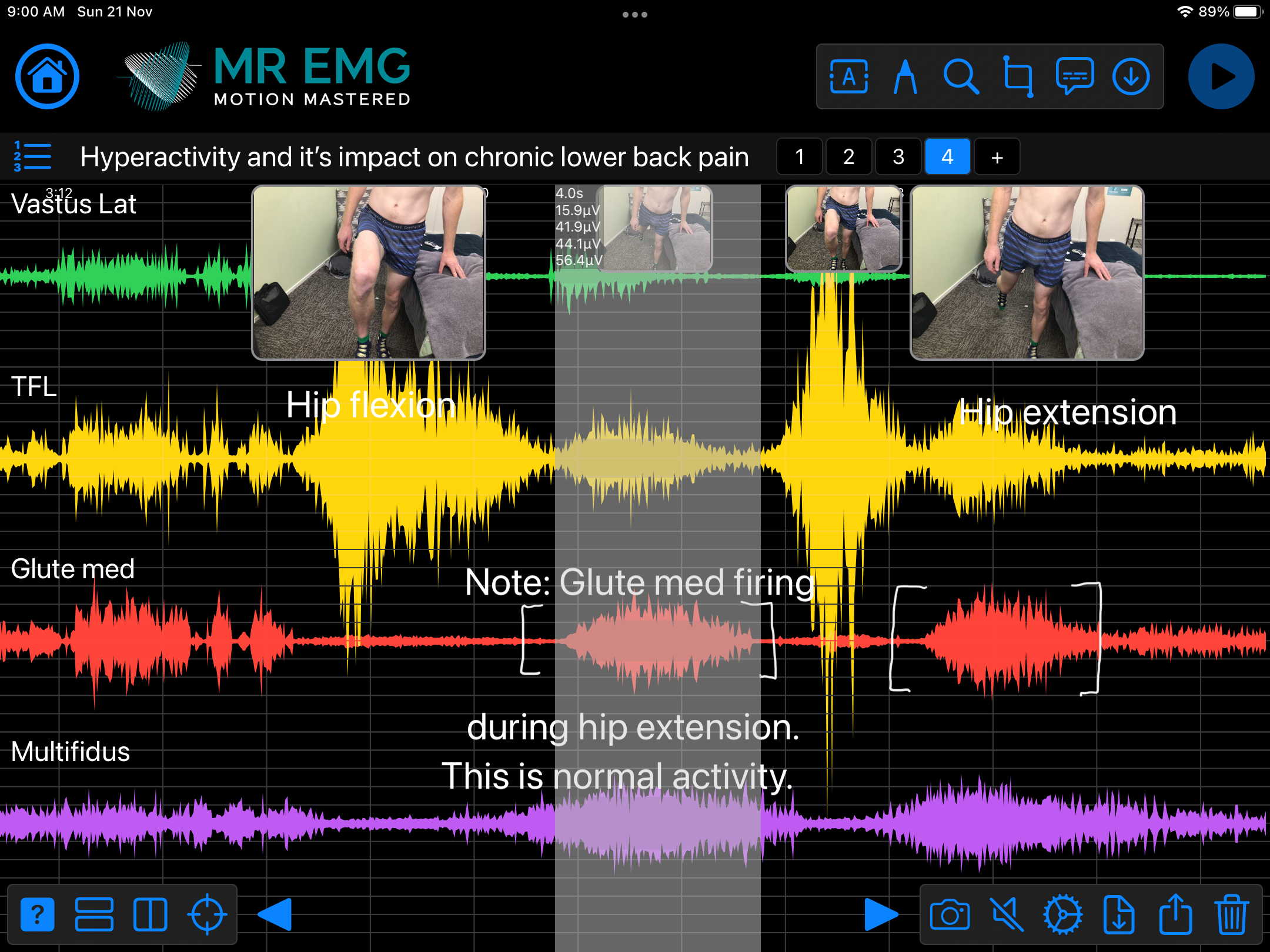
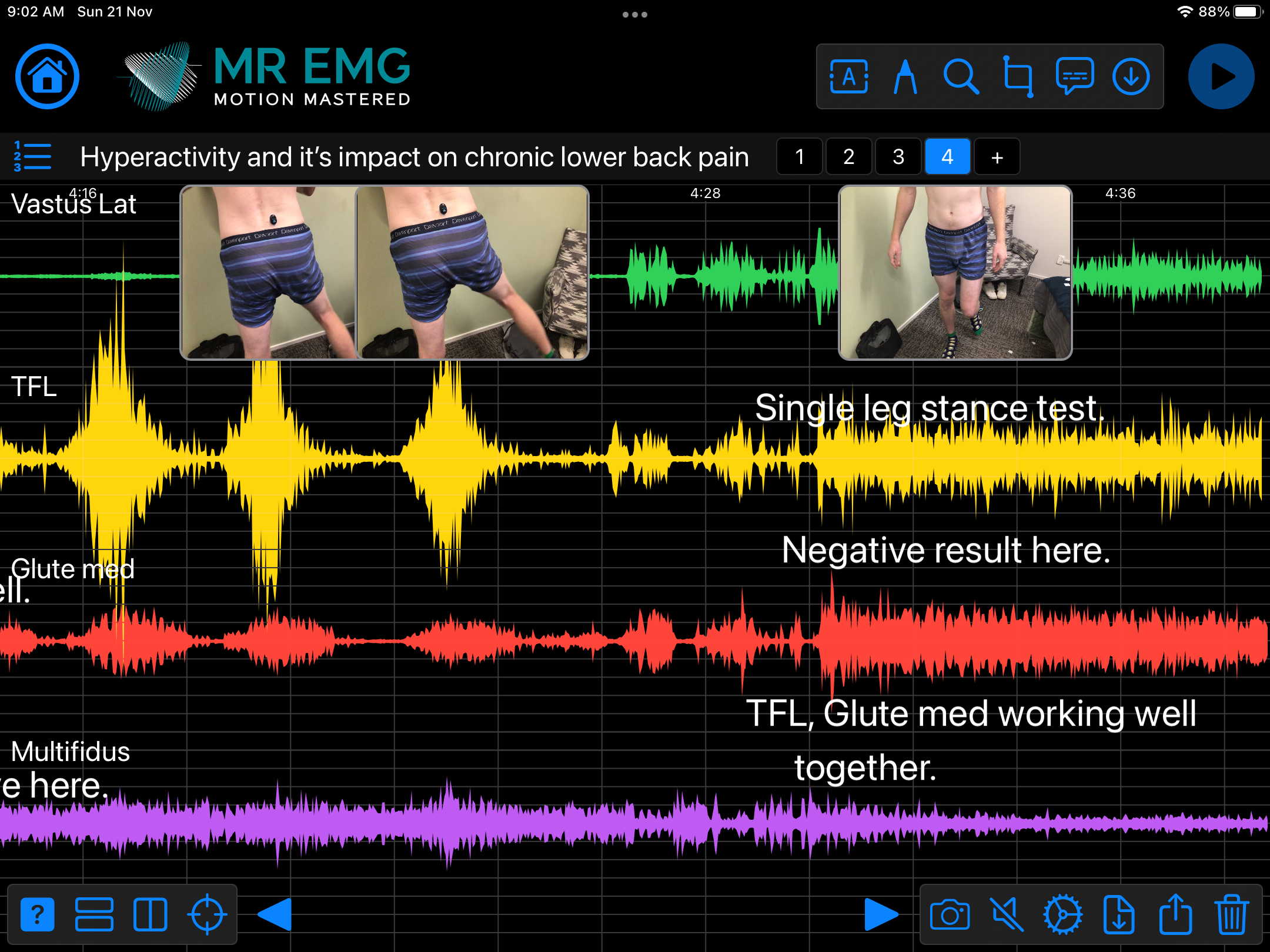
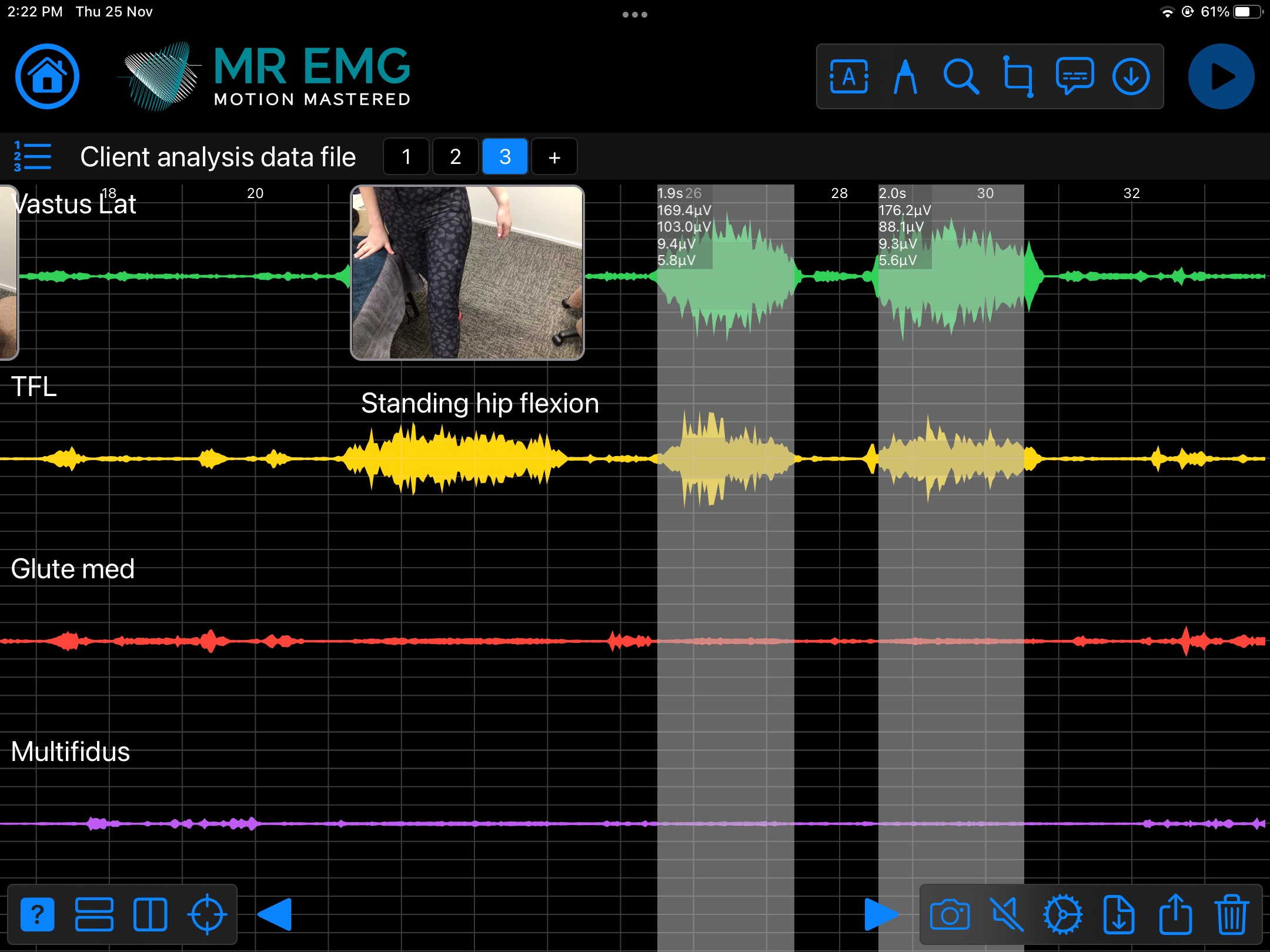
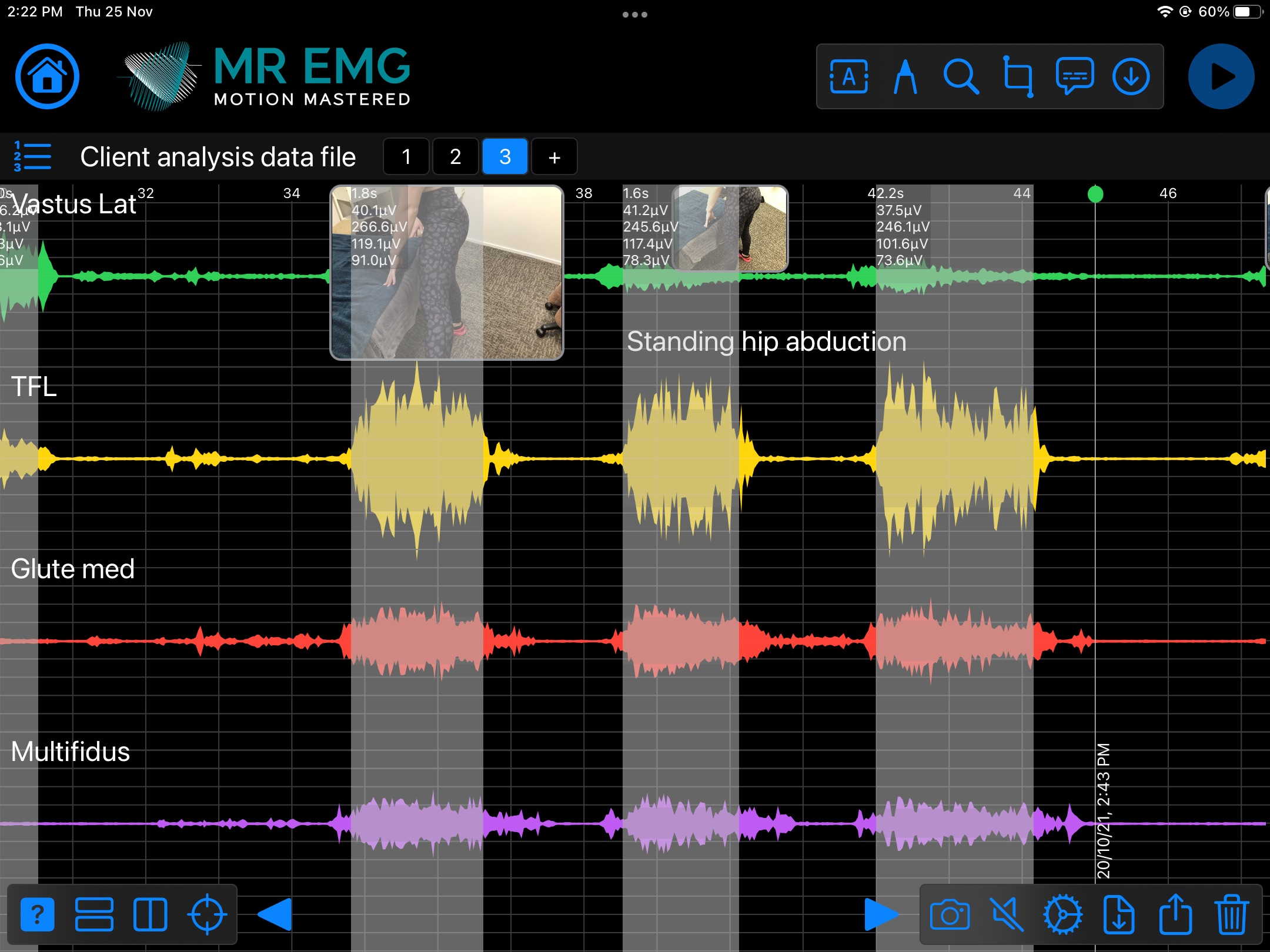
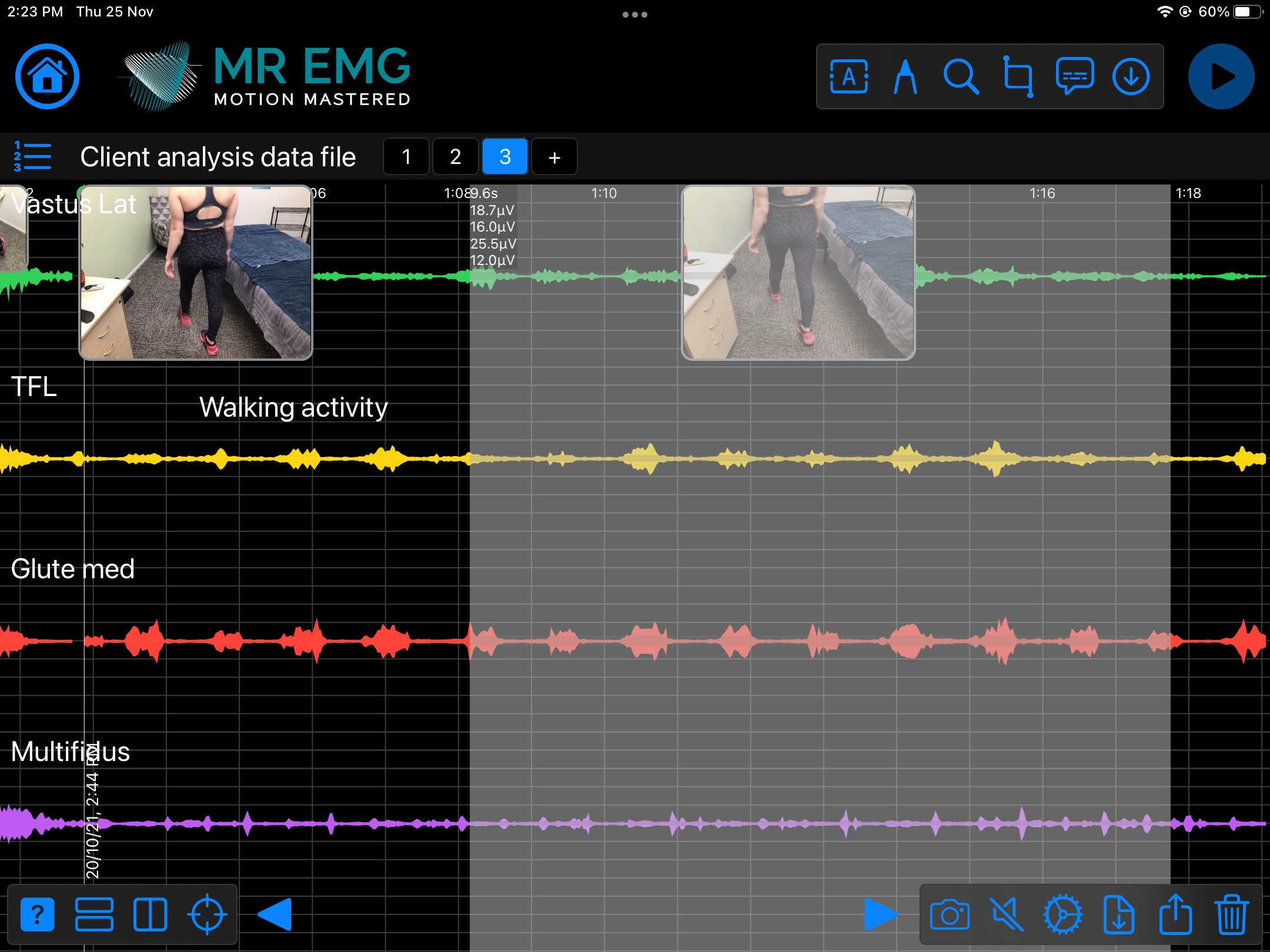
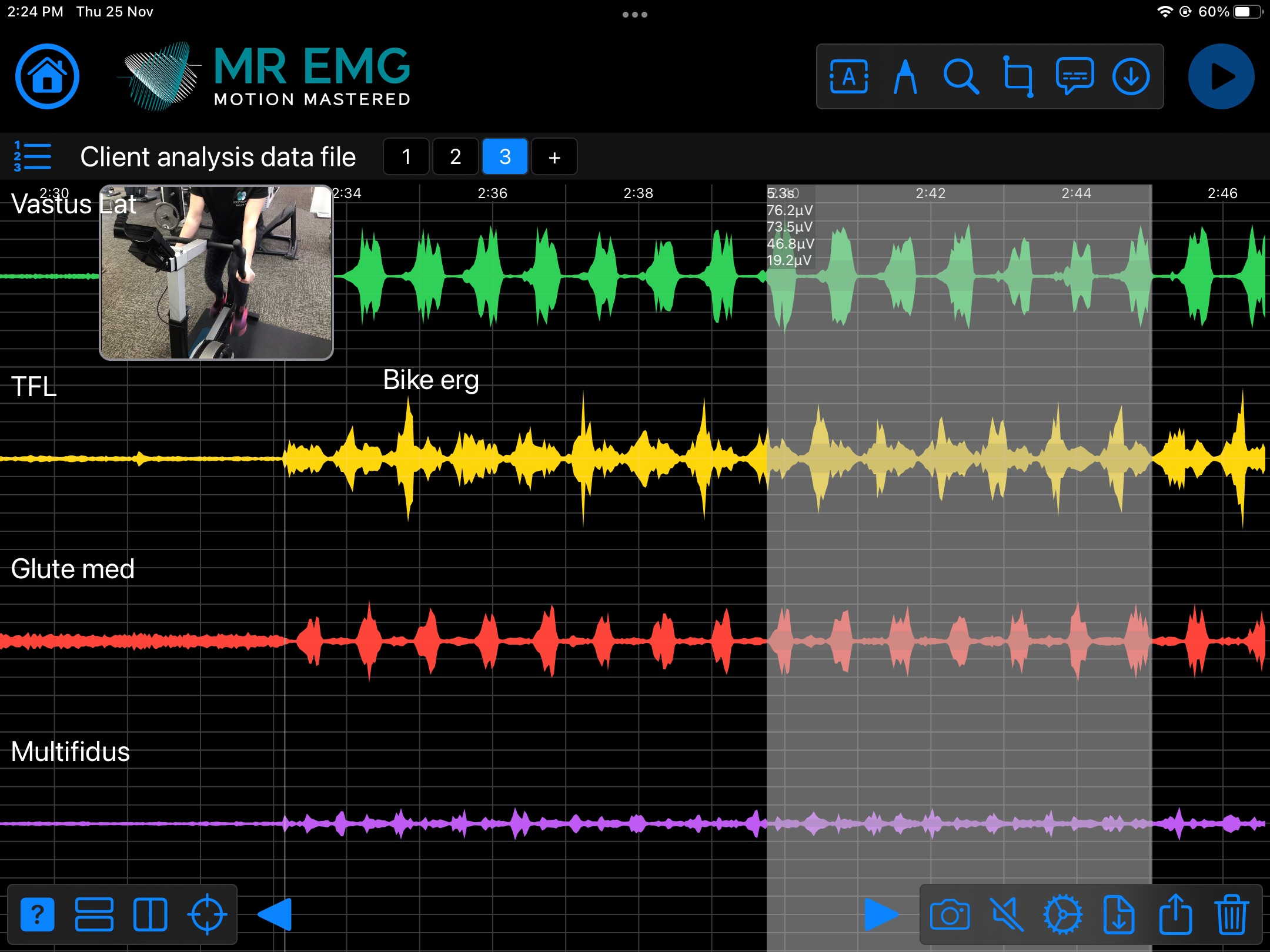
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing these muscles for


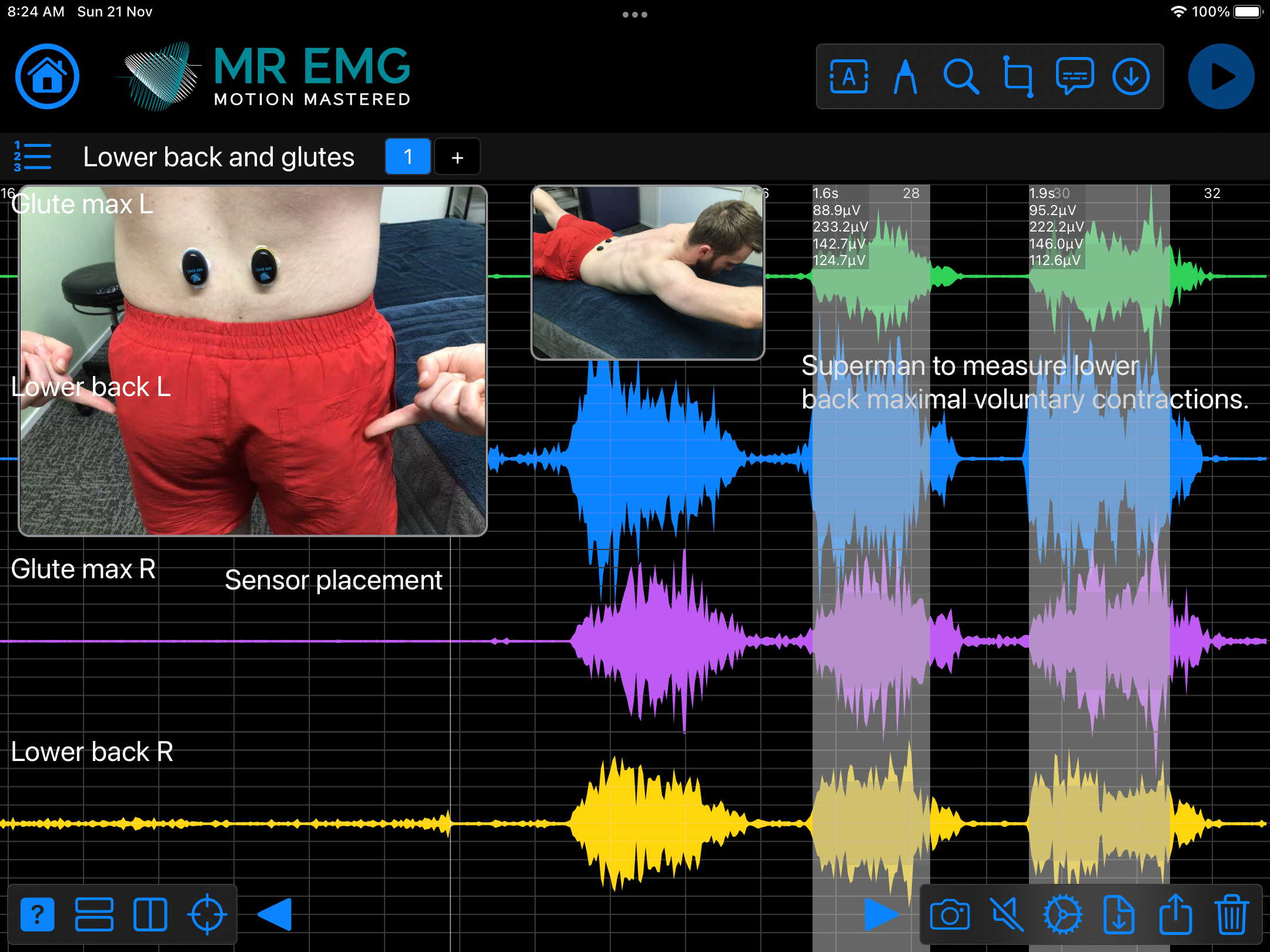
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider this muscle when testing
Consider this muscle when testing for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
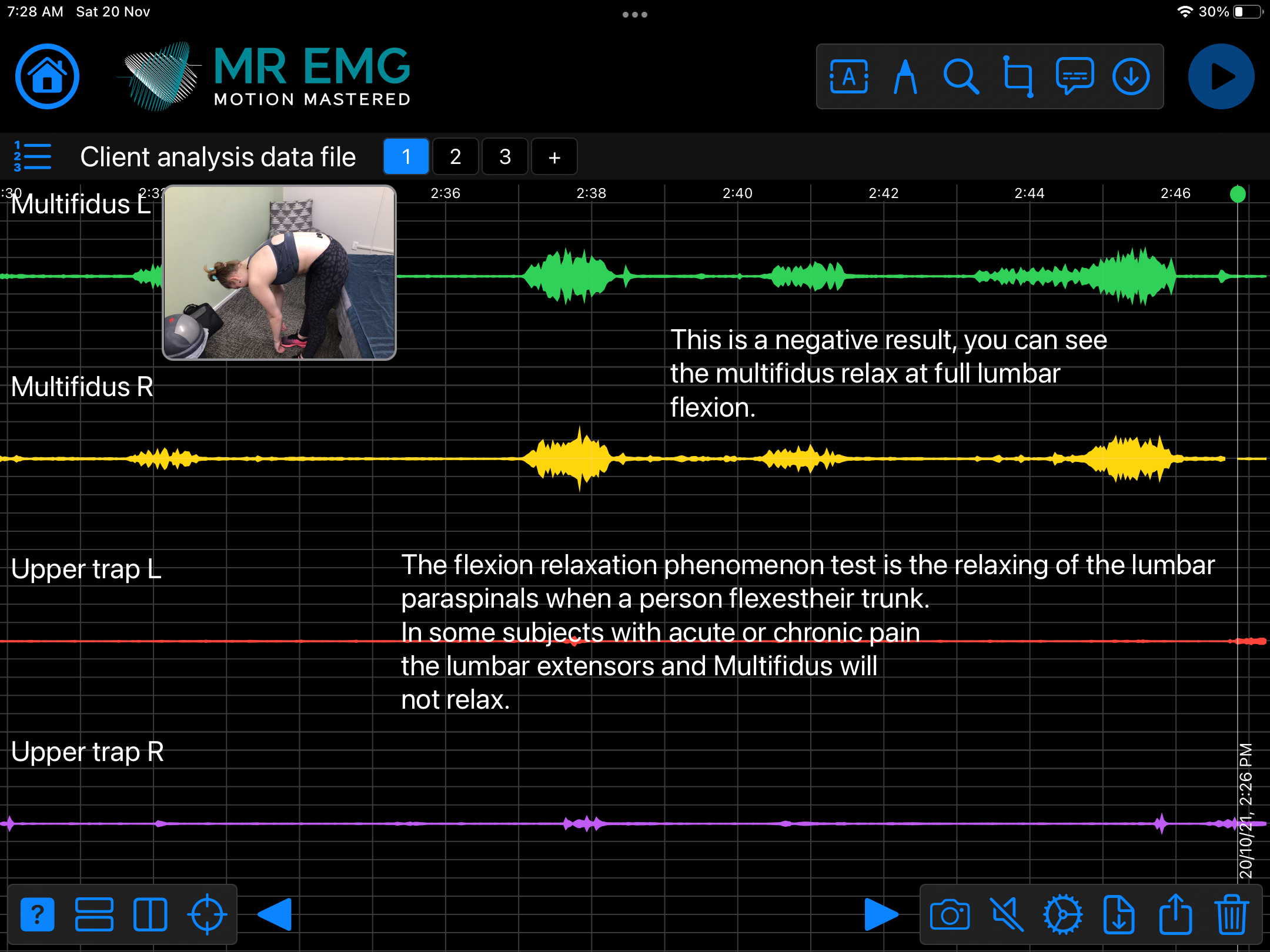
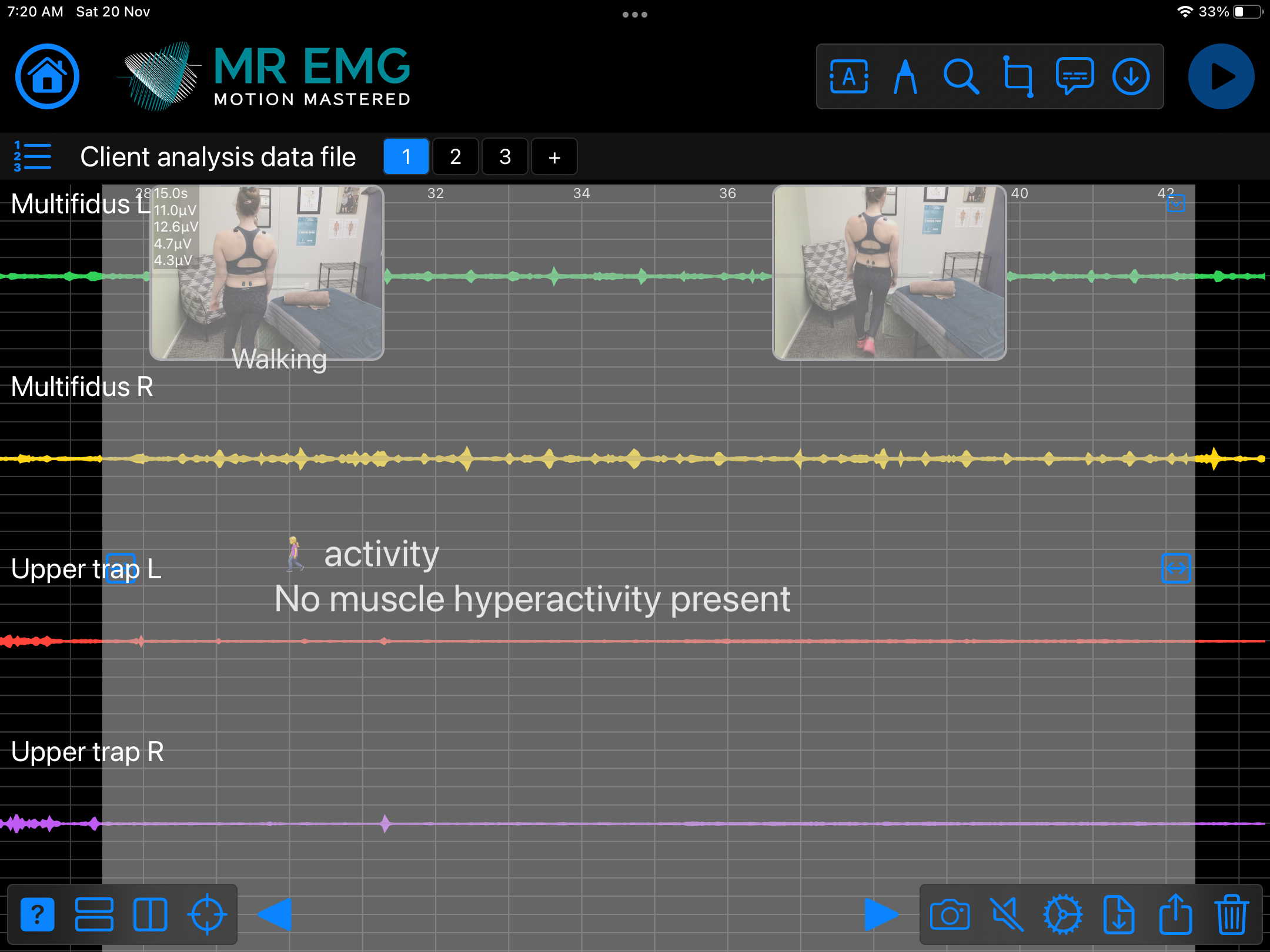
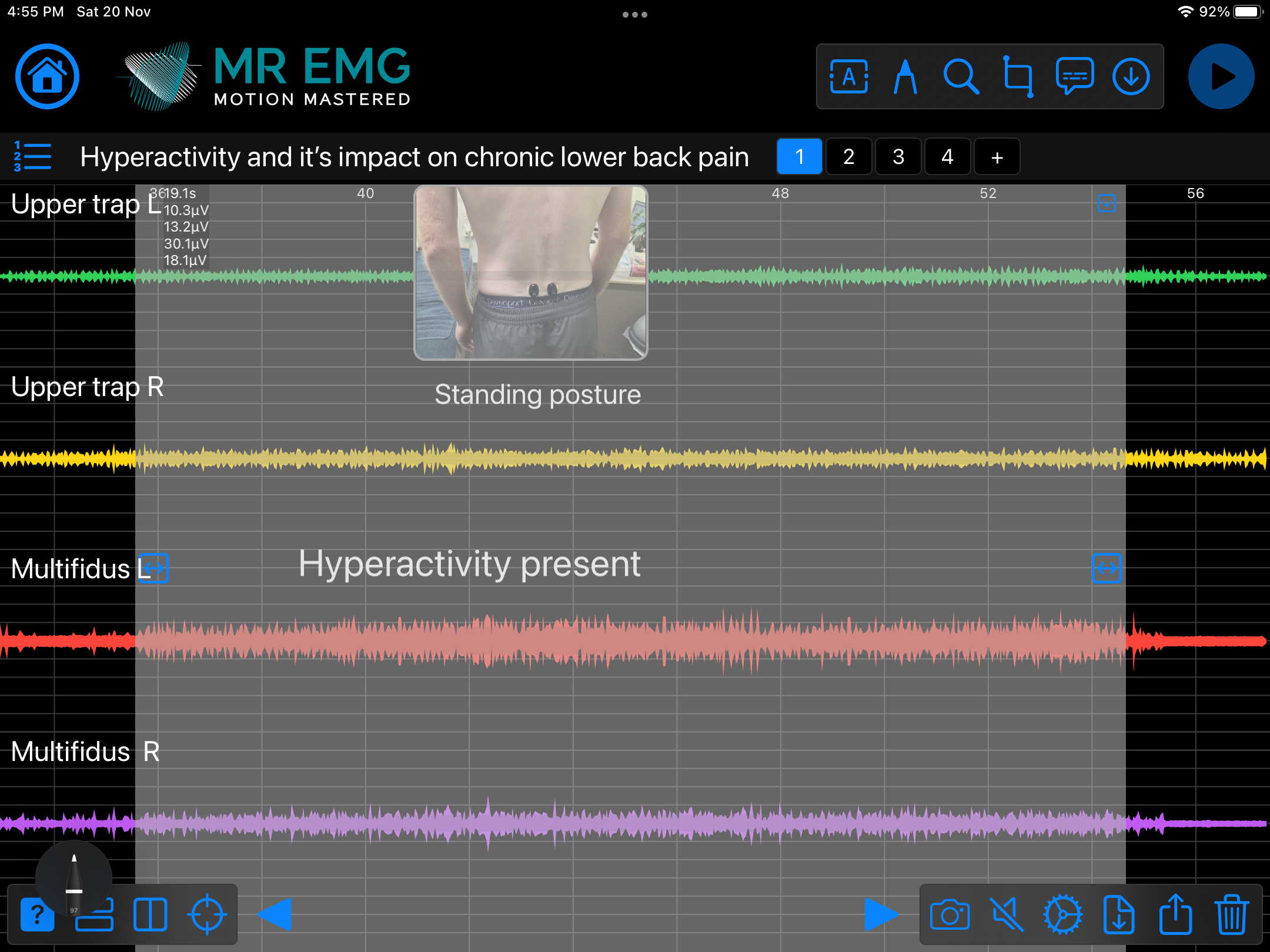
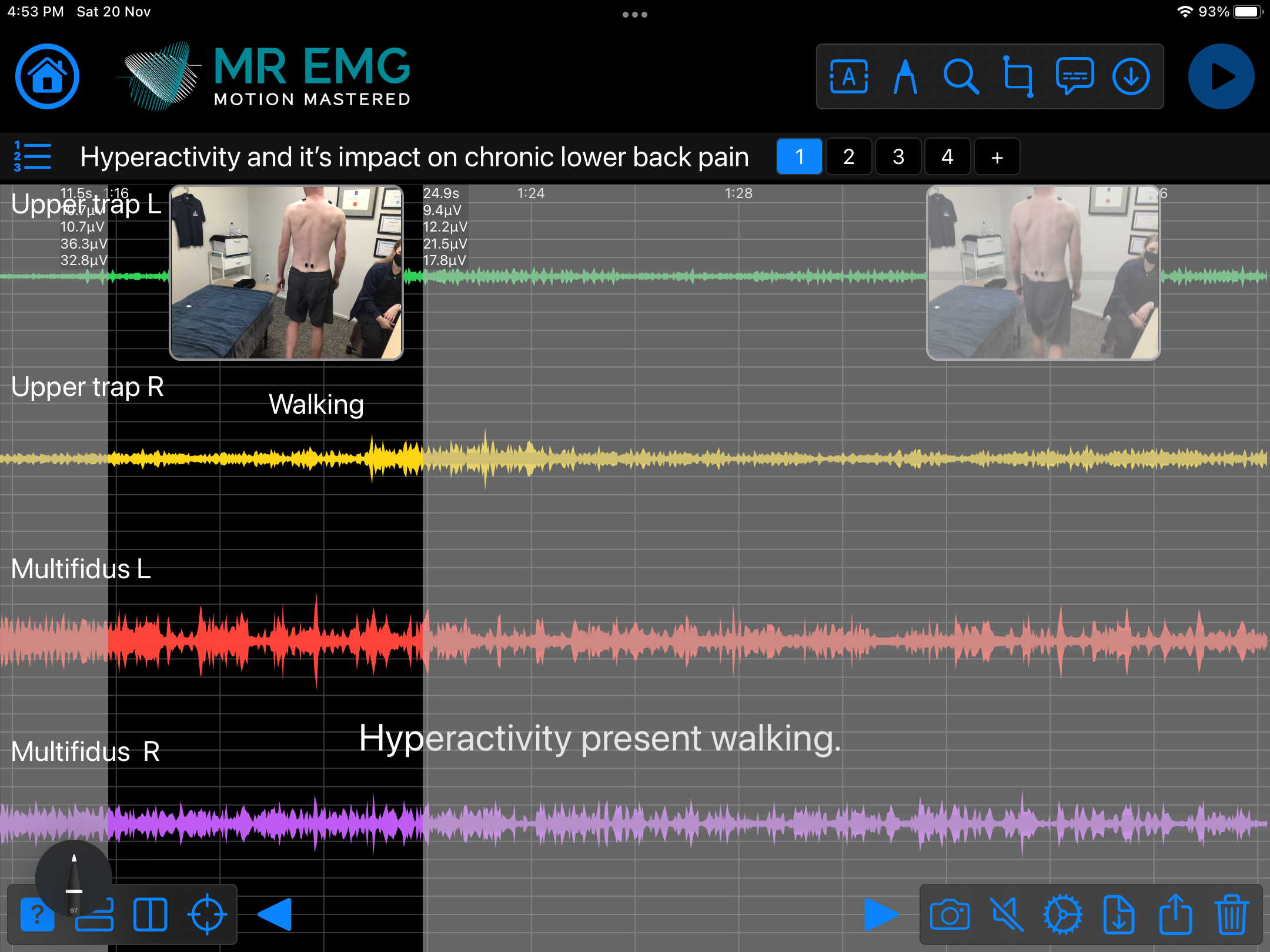
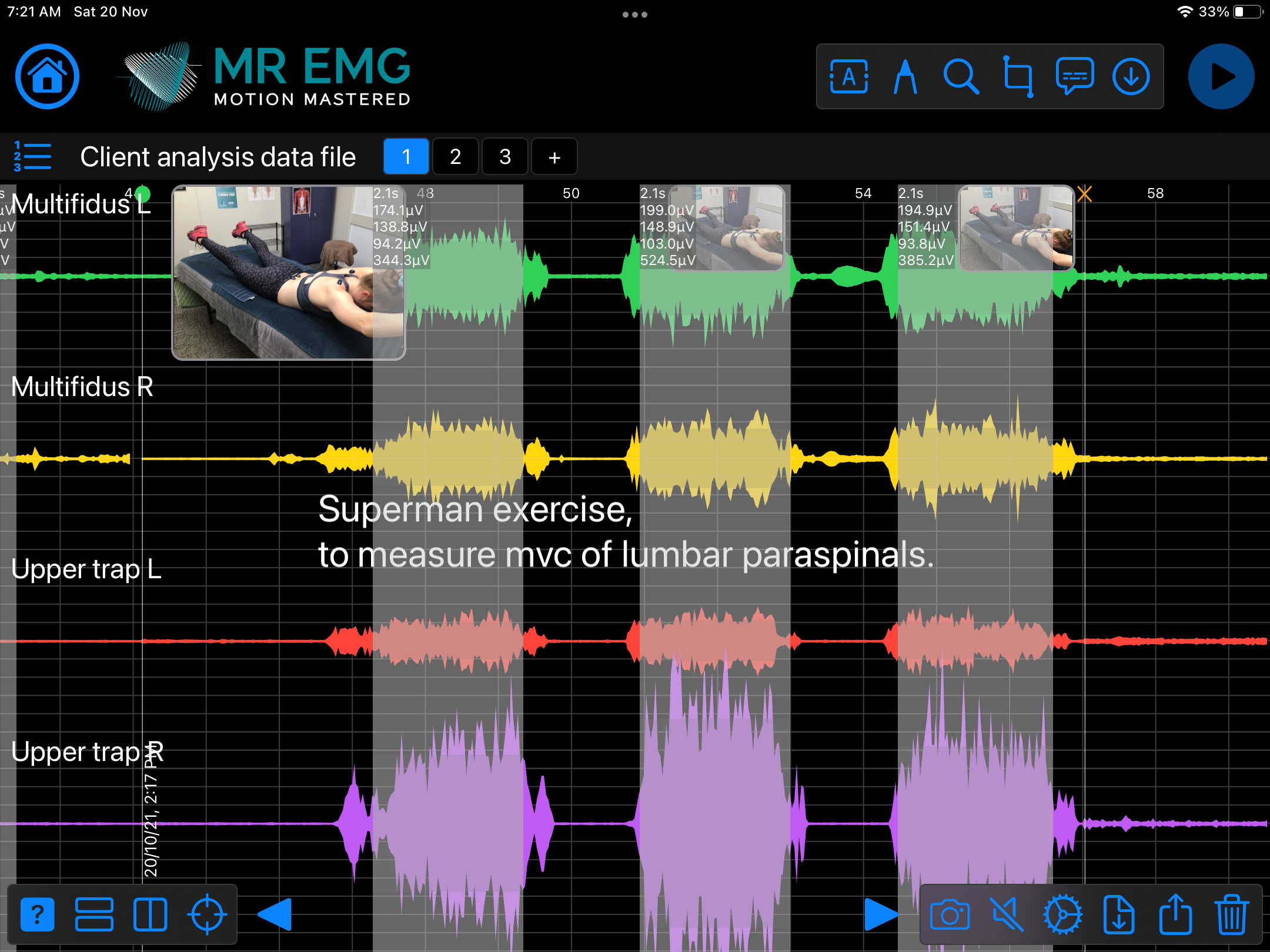
Consider testing these muscles for
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing these muscles for
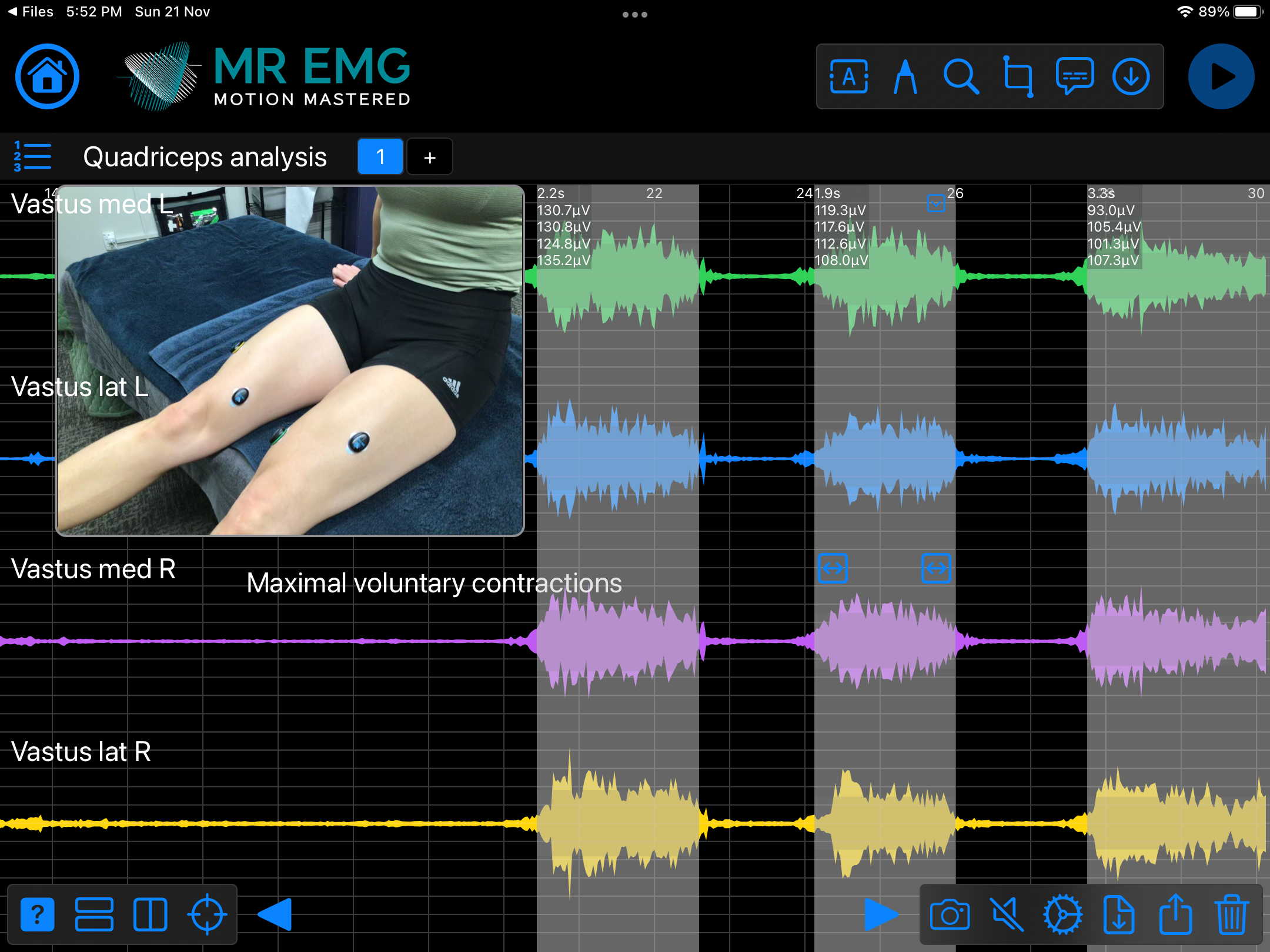
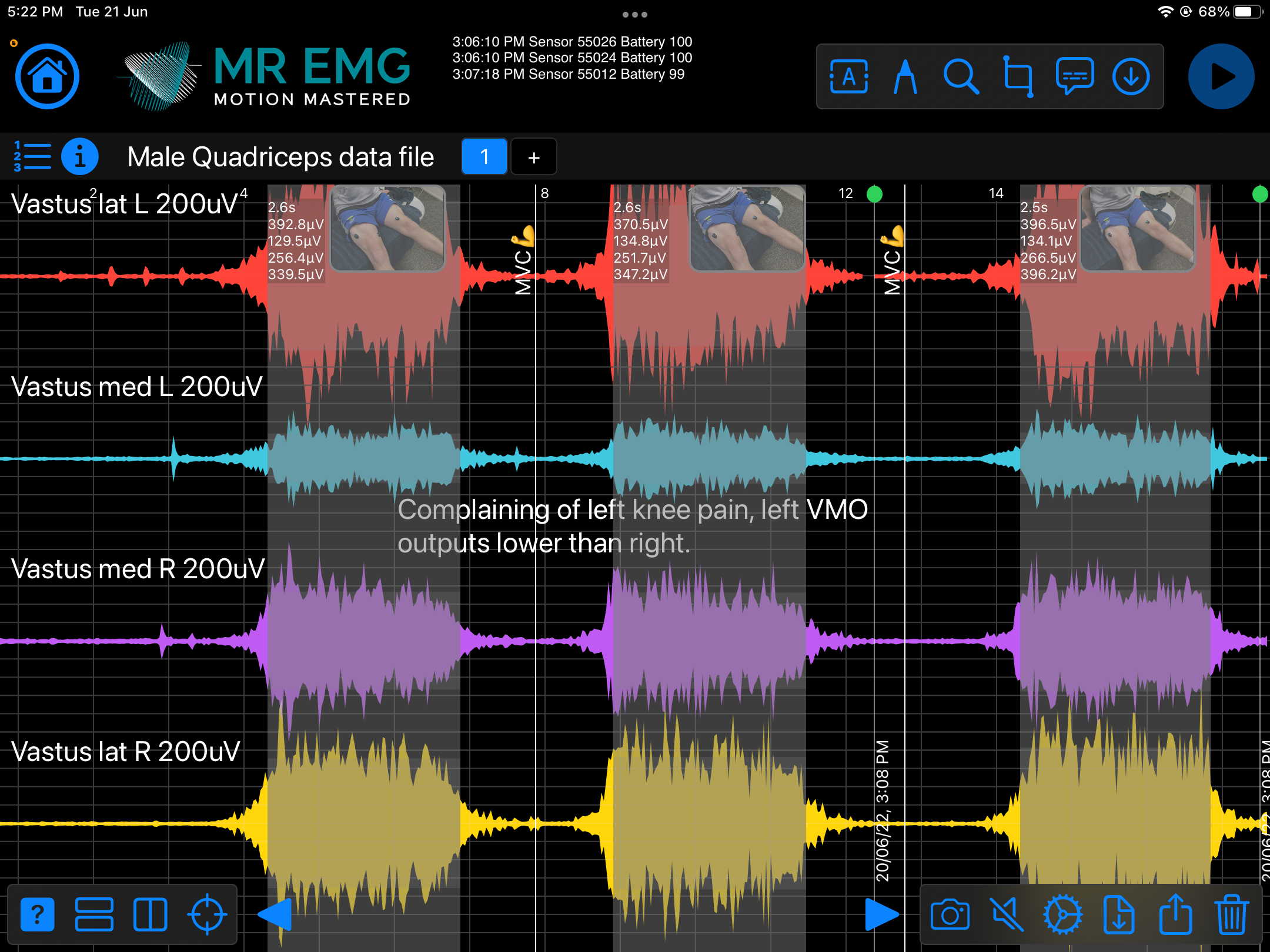
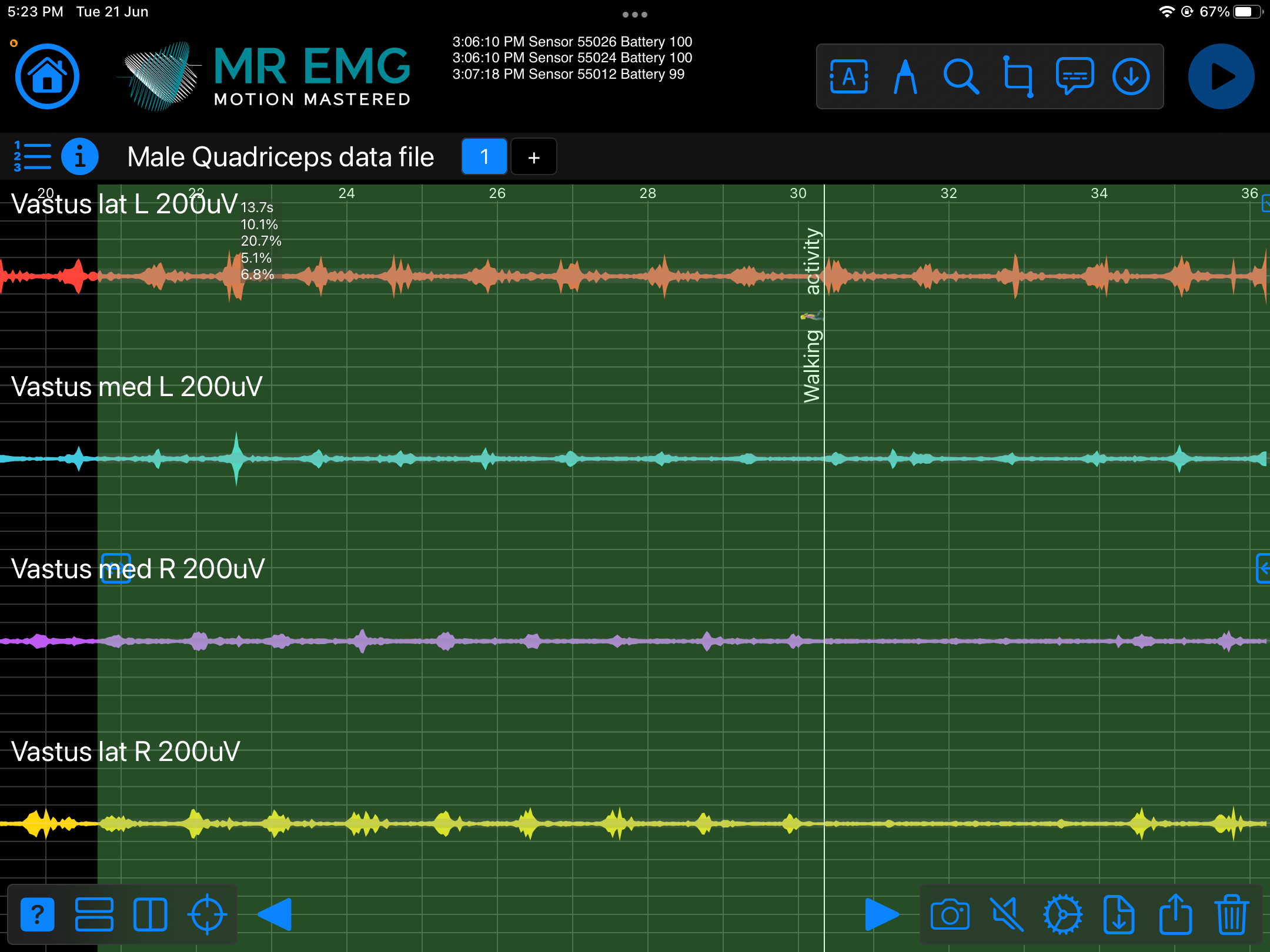
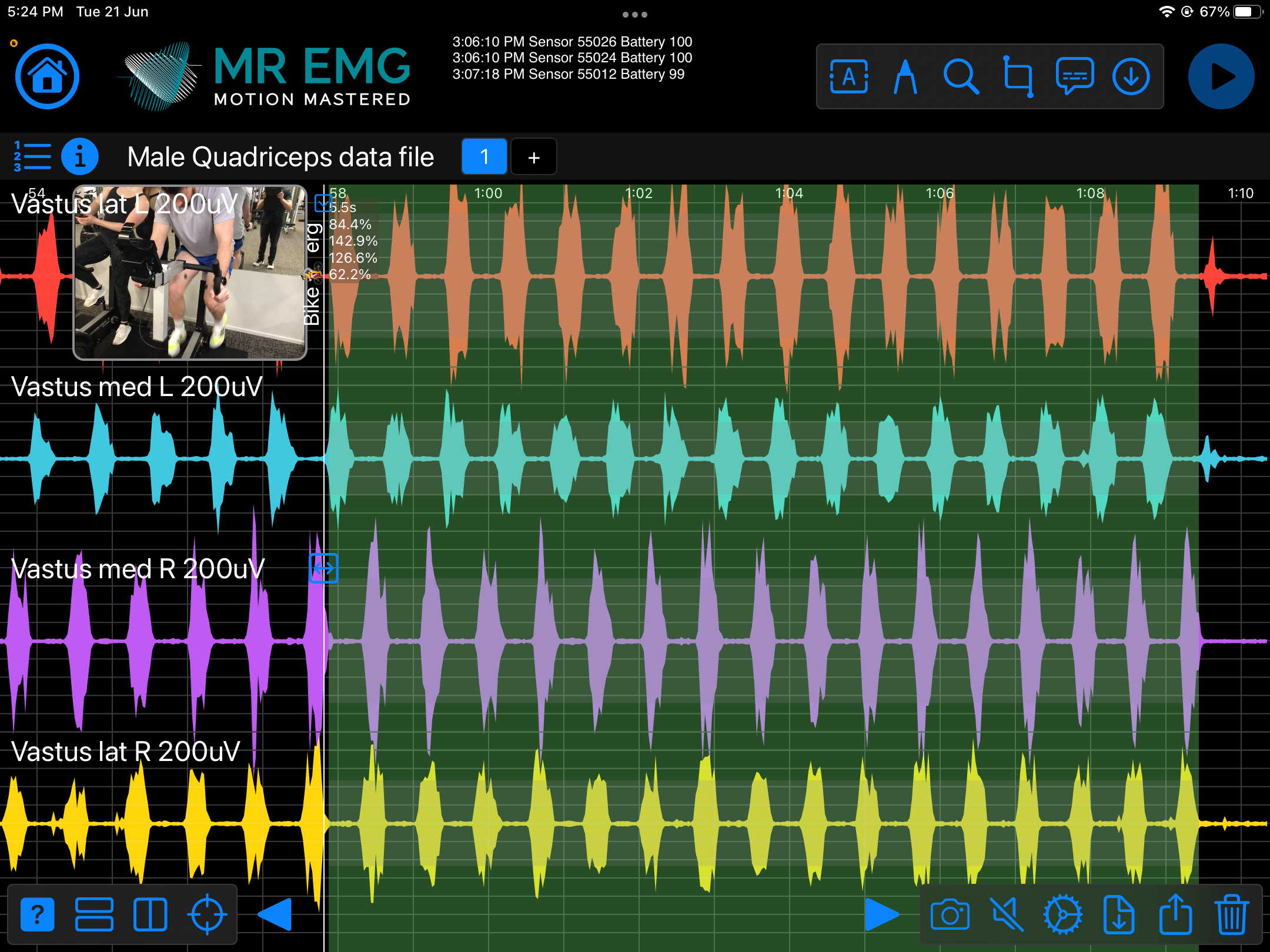
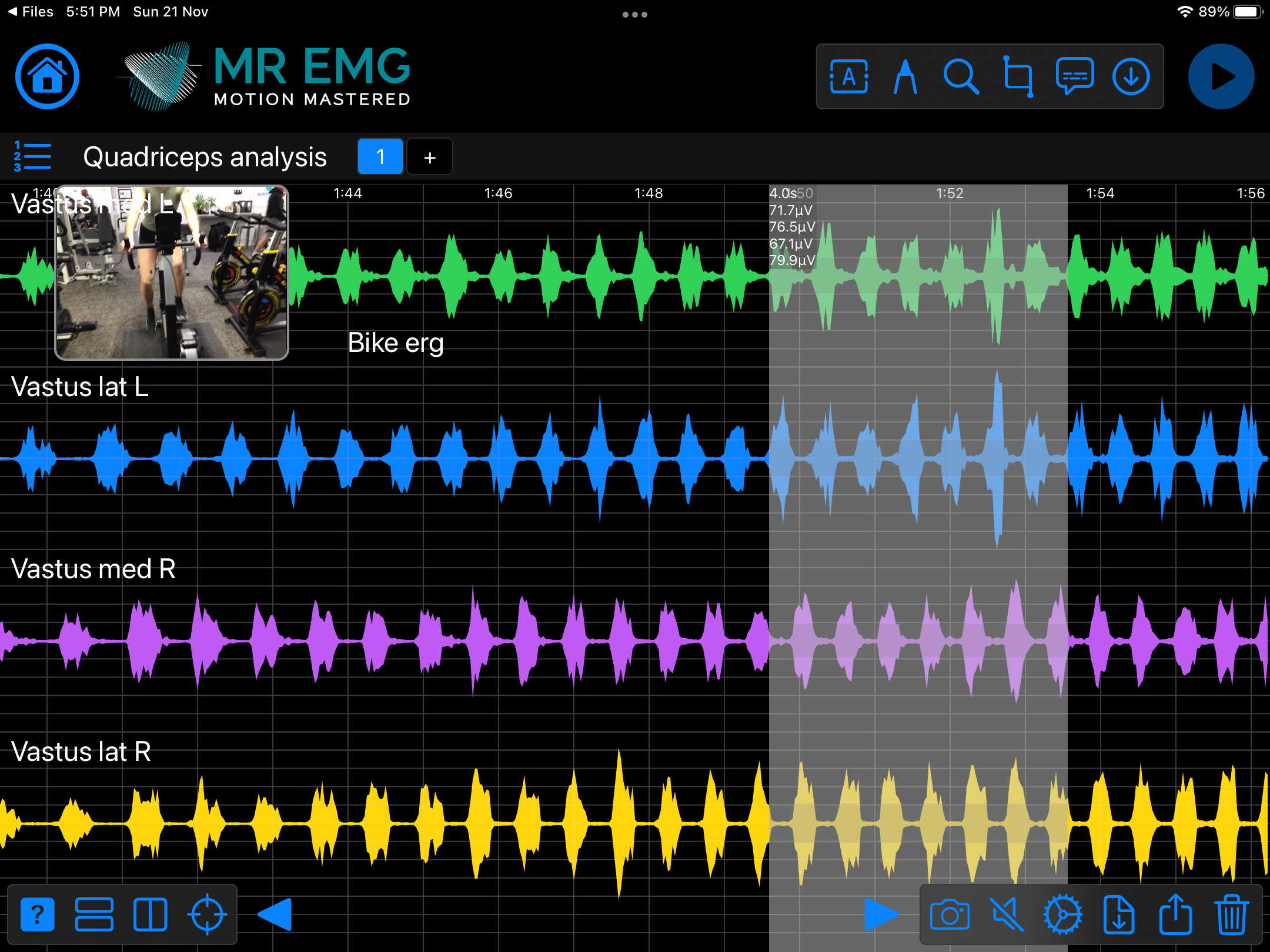
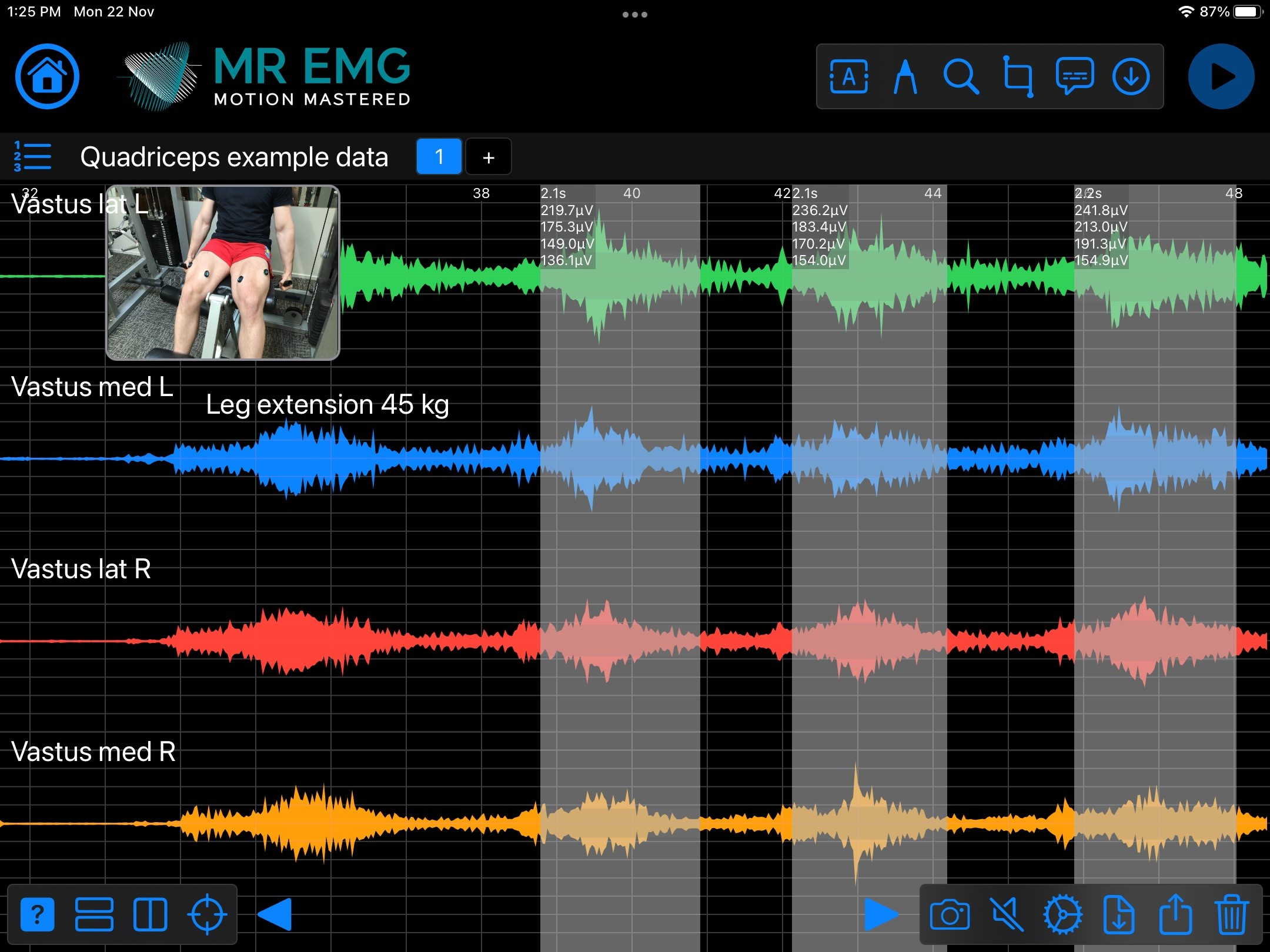
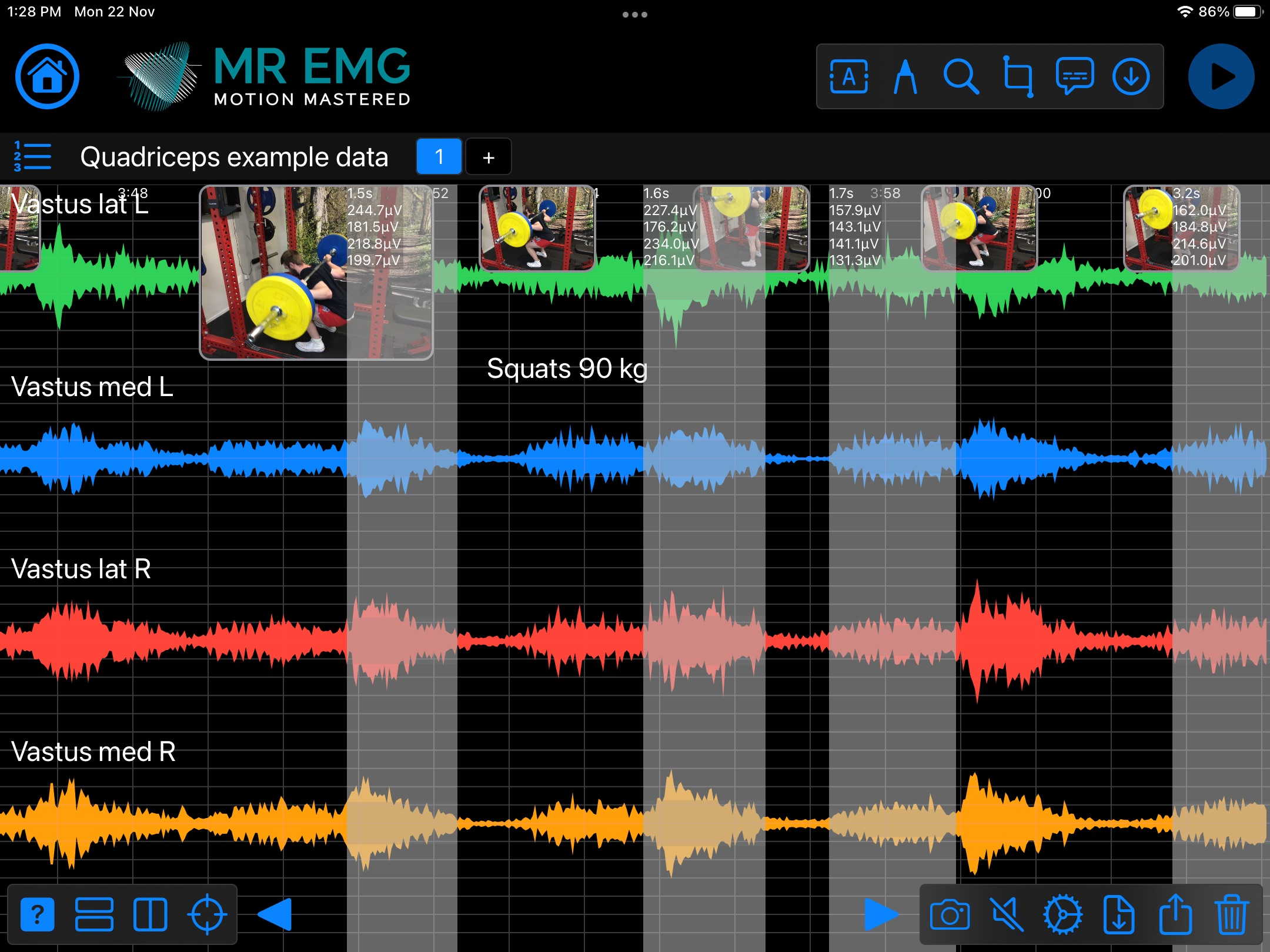
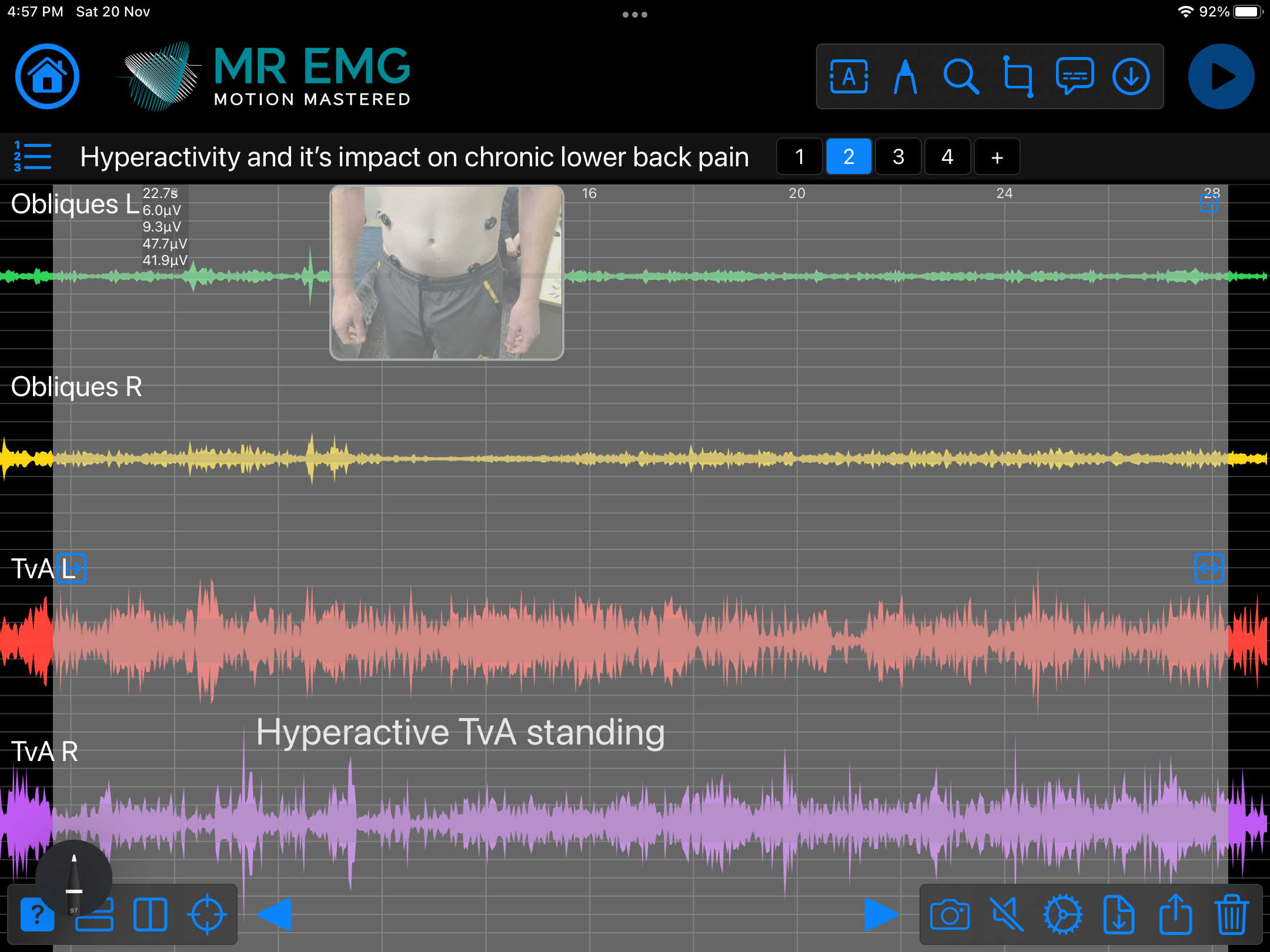
Consider testing this muscle for
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Example of four sensor shoulder analysis.
Example of four sensor shoulder analysis.
Example of two sensor shoulder analysis.
Example of four sensor shoulder analysis.
Example of four sensor shoulder analysis.
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing this muscle for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
Consider testing these muscles for:
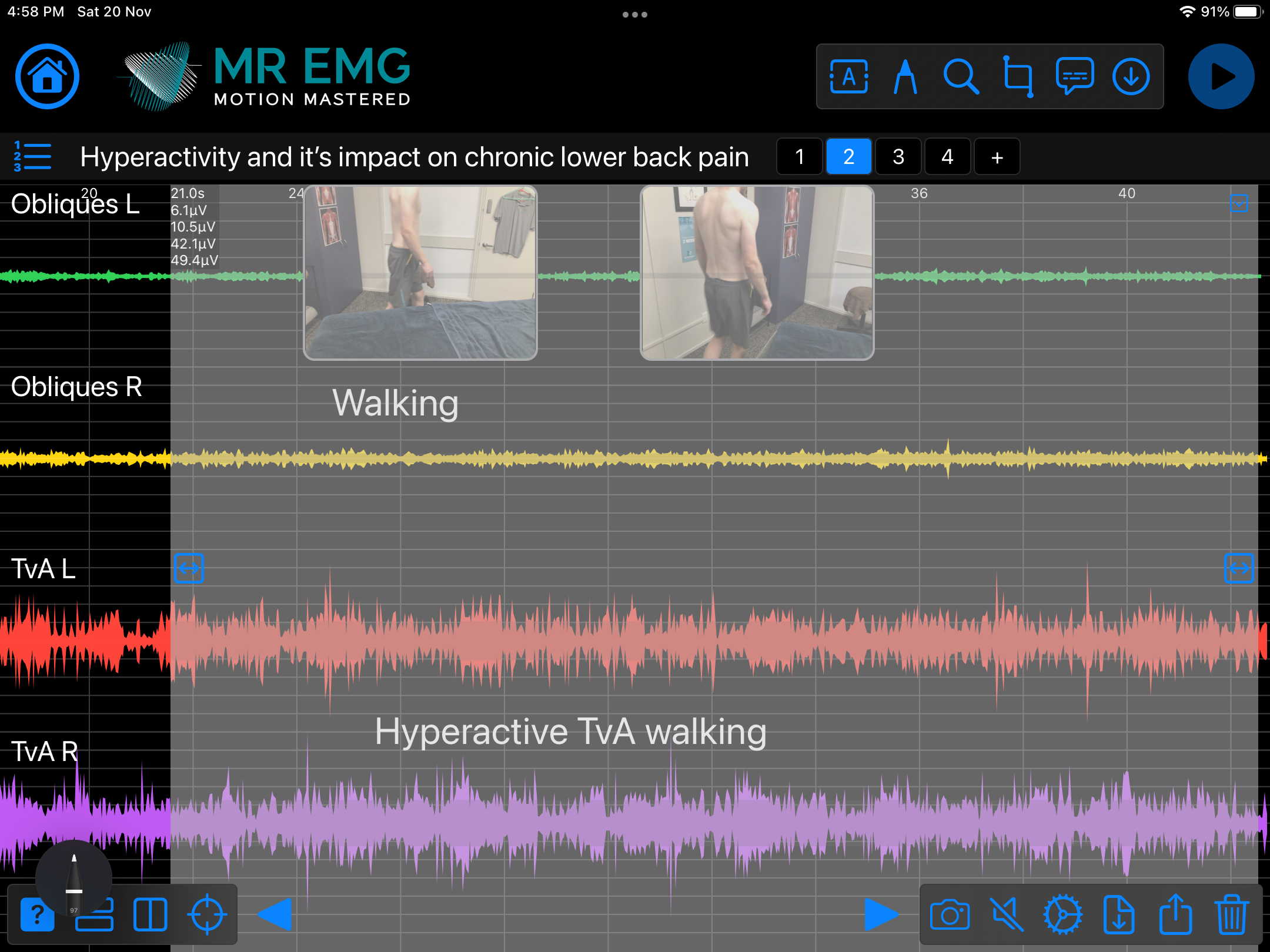
Consider testing this muscle for: